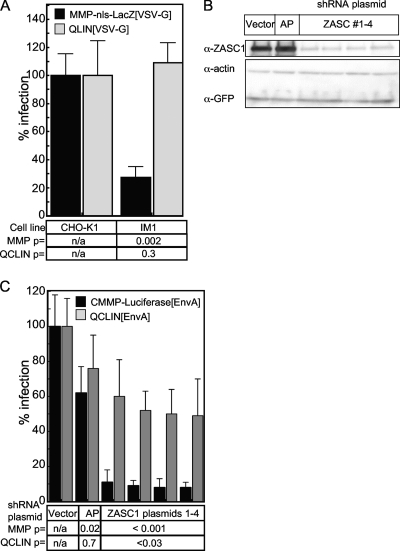
FIG. 4.
ZASC1 regulates expression from the MLV LTR promoter. (A) CHO-K1 or IM1 cells were challenged with the VSV-G-pseudotyped MLV vector MMP-nls-LacZ, which drives LacZ expression from the MLV-LTR promoter, or pQCLIN, a self-inactivating vector with defective LTRs and an internal HCMV promoter that drives LacZ expression. (B) Western blot analysis of HEK293T transiently transfected with GFP and ZASC1 expression plasmid and plasmids expressing either one of four shRNAs targeting the open reading frame of ZASC1, a control shRNA targeting secreted alkaline phosphatase (AP), or the empty shRNA vector. Cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting as described in Materials and Methods with rabbit antibodies against human ZASC1, human actin, and GFP. The blot is representative of three independent experiments. (C) HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with 80 ng of plasmids expressing either one of four shRNAs targeting the open reading frame of ZASC1, a control shRNA targeting secreted alkaline phosphatase (AP), or the empty shRNA vector along with 20 ng of an expression vector encoding the ASLV receptor TVA800 (2, 35). Three days posttransfection, cells were challenged with EnvA-pseudotyped MLV vectors, either CMMP-luciferase, which directs MLV LTR-driven firefly luciferase gene expression, or pQCLIN, which directs β-galactosidase expression from an internal HCMV promoter. Infection was monitored using chemiluminescent assays to detect reporter enzyme activities along with a chemiluminescent assay to measure relative viable cell numbers, and the data are reported as the ratio of reporter gene activity to the relative viable cell number observed, with CHO-K1 cells defined as 100% infection. The data shown are the average mean values obtained in an experiment performed with quadruplicate samples, and each is representative of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate the standard deviations of the data. P values were calculated using a standard Student's t test.