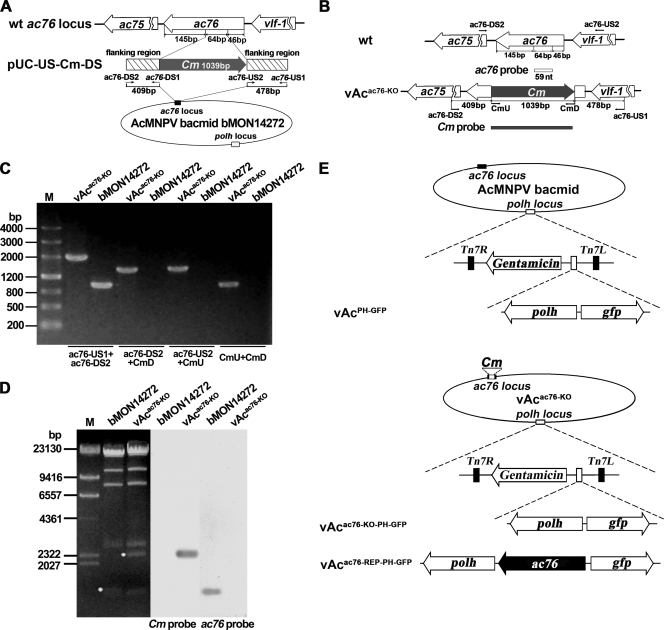
FIG. 3.
Construction of the ac76-knockout bacmid. (A) Strategy for construction of an ac76-knockout bacmid using the AcMNPV bacmid system. A 64-bp sequence of the ac76 ORF was deleted and replaced with the Cm gene sequence. (B) Positions of primer pairs and probes used to confirm the disruption of ac76 and the insertion of the Cm gene. (C) PCR analysis to determine the presence or absence of sequence modification in bMON14272 and vAcac76-KO. The primer pairs are shown below the panel, and the templates are noted above each lane. (D) Southern blot analysis of the bMON14272 bacmid and vAcac76-KO. The ac76 probe and the Cm gene probe were used to confirm the deletion of ac76 and its replacement by the Cm gene. (E) Schematic diagram of the recombinant viruses vAcPH-GFP, vAcac76-KO-PH-GFP, and vAcac76-REP-PH-GFP showing the polh and gfp genes inserted in the polh locus by Tn7-mediated transposition. The ac76 ORF that was inserted into vAcac76-KO was controlled by its own promoter.