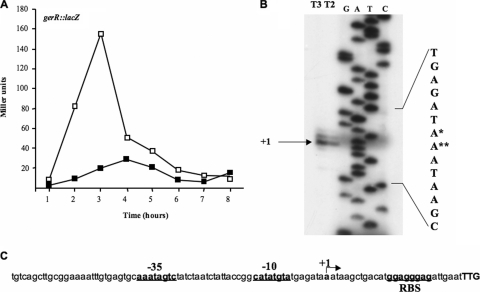
FIG. 1.
(A) gerR-directed β-galactosidase synthesis in an otherwise wild-type strain (open squares) and in a spoIIID null background (closed squares). Samples were collected at various times after the onset of sporulation. Enzyme activity is expressed in Miller units. Data are the means of three independent experiments. (B) Primer extension analysis of the gerR promoter region performed with total RNA extracted from sporulating cells 2 and 3 h after the onset of sporulation (T2 and T3). Primer extension and sequencing reactions were primed with the synthetic oligonucleotide gerR PE (Table 2). Although this oligonucleotide primed the sequence of the template strand, the sequence of the coding strand is shown for consistency with panel C. The single and double asterisks indicate the more and less frequently used transcriptional start point, respectively. (C) gerR promoter region. The translational start site (TTG) is shown in boldface capital letters, the transcriptional start site is indicated as +1, and the putative promoter and ribosomal binding site (RBS) sequences are underlined boldface lowercase letters.