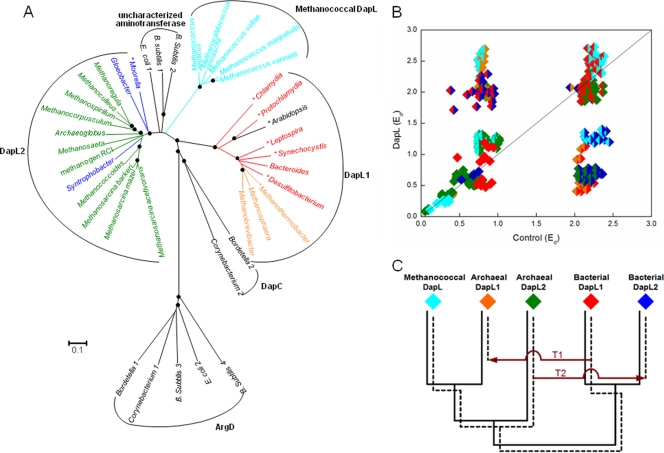
FIG. 5.
Phylogenetic analyses of the DapL homologs. Red, bacterial DapL1; blue, bacterial DapL2; orange, archaeal DapL1; green, archaeal DapL2; cyan, methanococcal DapL. (A) Phylogenetic tree constructed by the minimum evolution method using the MEGA4 program. Scale bar = 0.1 amino acid substitution per site. Organisms whose enzymes have biochemically confirmed DapL activity are indicated by an asterisk (18, 24). Filled circles at branch points indicate ≥70% replication for 1,000 bootstraps. The grouping of DapL1 and DapL2 is based on the findings of Hudson et al. (18). Several aminotransferases from E. coli, B. subtilis, Bordetella parapertussis, and C. glutamicum, which are organisms that are known to lack DapL activity, were included to provide an overall context. The locus tags of the sequences used in the phylogenetic analysis are as follows: Protochlamydia, pc0685; Chlamydia, CT390; E. coli 1, b2379; E. coli 2, b3359; Gloeobacter, glr4108; B. subtilis 1, BSU37690; B. subtilis 2, BSU13580; B. subtilis 3, BSU11220; B. subtilis 4, BSU03900; Bacteroides, BF2666; Bordetella 1, BPP2543; Bordetella 2, BPP1996; Synechocystis, sll0480; Leptospira, LIC12841; Methanococcoides, Mbur1013; Methanosarcina barkeri, Mbar_A2605; Methanosphaera, Msp0924; Methanospirillum, Mhun2943; Moorella, Moth0889; Archaeoglobus, AF0409; Methanosarcina acetivorans, MA1712; Methanosarcina mazei, MM2649; Methanosaeta, Mthe0801; Methanothermobacter, MTH52; Corynebacterium 1, NCgl1343; Corynebacterium 2, NCgl1058; Desulfitobacterium, Dhaf1761; Arabidopsis, AT4G33680; Syntrophobacter, Sfum0054; Methanocorpusculum, Mlab0633; Methanoculleus, Memar1915; Methanobrevibacter, Msm1455; methanogen RCI, RCIX1962; Methanoregula, Mboo2096; Methanococcus aeolicus, Maeo1494; Methanococcus vannielii, Mevan0840; Methanococcus maripaludis, MMP1527; Methanocaldococcus jannaschii, MJ1391; and Methanococcus voltae, Mvol0315. (B) RED plot of DapL homologs. Intradomain comparisons within each DapL subgroup are indicated by diamonds that are a single color. Comparisons of different subgroups are indicated by diamonds that are two colors. (C) Hypothetical gene tree illustrating the proposed evolutionary history of DapL homologs. The solid lines show the organismal phylogeny in the absence of LGT. The dashed lines show the gene tree for DapL. T1 indicates the acquisition of bacterial DapL1 by archaea, and T2 indicates the acquisition of archaeal DapL2 by bacteria.