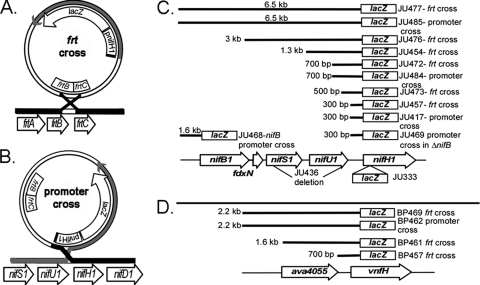
FIG. 1.
Map of the genes analyzed in these studies. Two possible single-crossover events between plasmids bearing the promoter-lacZ fusions are shown. (A) Recombination between the frtBC genes on the vector and in the chromosome resulted in a strain in which only the promoter fragment provided in the plasmid drove expression of lacZ. The chromosomal nifHDK1 structural gene region was unchanged. (B) Recombination between the nifH1 promoter fragment in the plasmid and the chromosomal promoter placed lacZ under the control of the full, normal nifH1 upstream region, including nifBSU1. The chromosomal nifHDK1 structural genes are under the control of only the plasmid-borne promoter fragment. (C) Diagram of the nifH1 region with the strain names and sizes of the tested promoter fragments (not drawn to scale). Strain JU436 has a deletion of the nifSU coding region as indicated. (D) Diagram of the vnfH region with the strain names and sizes of the tested promoter fragments.