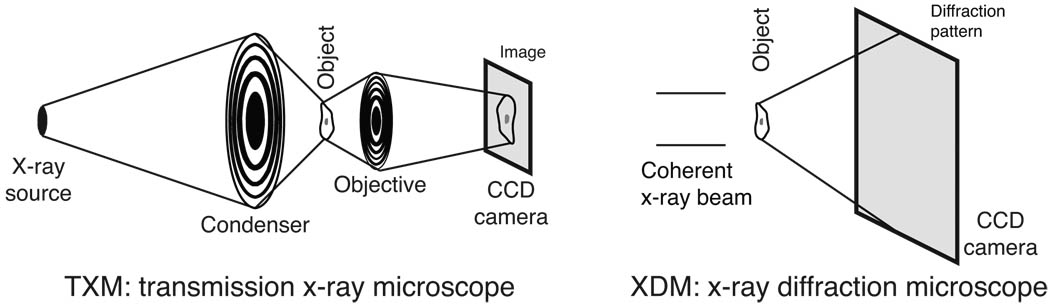
Fig. 4.
Schematic of the two x-ray imaging systems considered in simulations. In the TXM or transmission x-ray microscope at left, incoherent brightfield imaging is assumed where the numerical aperture of the condenser is 1.5 times the numerical aperture of the objective lens; a magnified image is recorded on a detector such as a CCD. The TXM objective is a zone plate with 30 nm outermost zone width and 10% diffraction efficiency. In XDM or x-ray diffraction microscopy at right, the specimen is assumed to be illuminated by a fully coherent beam and the far-field x-ray diffraction pattern is recorded on a detector such as a CCD. A reconstructed image is obtained by computational phasing of the coherent diffraction pattern.