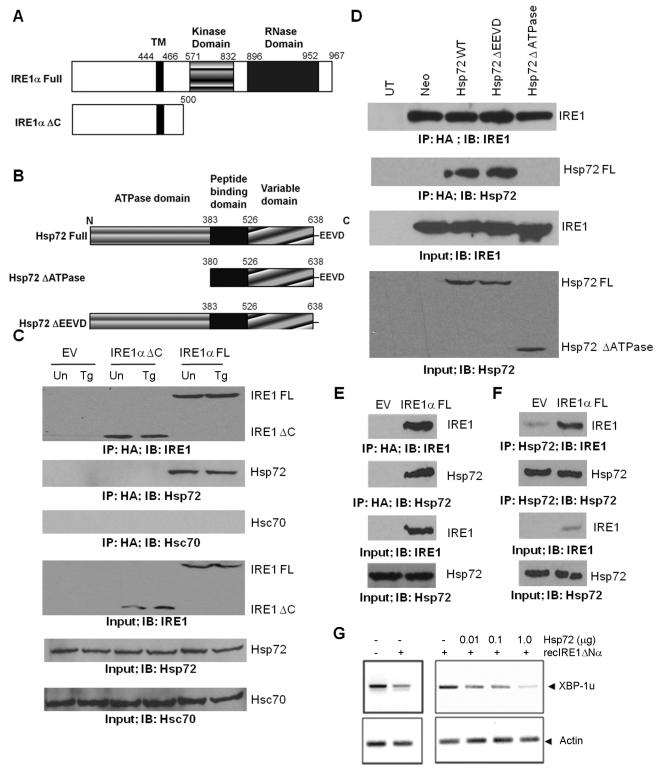
Figure 5. Hsp72 forms a protein complex with IRE1α, and the ATPase domain of Hsp72 is critical for IRE1α binding.
(A) Schematic diagram for IRE1α structure domains and expression constructs. (B) Schematic diagram for Hsp72 structure domains and expression constructs. (C) Hsp72 expressing PC12 cells (Hsp72) were transfected with empty vector (EV) or expression vectors for IRE1α FL-HA or IRE1α ΔC-HA. After 24 h, cells were either untreated (Un) or treated with (0.25 µM) Tg for 12 h and then the co-precipitation of Hsp72 with IRE1α FL-HA or IRE1α ΔC-HA was evaluated by IP and Western blot. (D) PC12 cells expressing the indicated Hsp72 constructs were transfected with IRE1α FL-HA. Lysate from untransfected PC12 cells (UT) was used as a negative control. Co-precipitation of wild-type, ΔATPase, and ΔEEVD mutant of Hsp72 with IRE1α FL-HA was evaluated by IP and Western blot. (E) HEK 293 cells were transiently transfected with IRE1α FL-HA expression vector or empty vector (EV). After 48 h, IRE1α FL-HA was immunoprecipitated and its association with endogenous Hsp72 was assessed by Western blot. (F) Endogenous Hsp72 was immunoprecipitated from HEK 293 cells transiently transfected with IRE1α FL-HA expression vector or empty vector (EV), and its association with IRE1α was determined by Western blot analysis. Input: 5% of the total cell lysate used for IPs. (G) Indicated concentrations of recombinant Hsp72 was incubated with 1 µg recIRE1ΔNα for 1 h at 30°C in the presence of ATP, and 10 µg total mRNA. The ribonuclease activity of IRE1α was analyzed by RT-PCR by using regular XBP1 mRNA splicing primers, evidenced as decreased PCR product of the nonspliced fragment. Actin was monitored as control (lower panel). A representative of three independent experiments is shown.