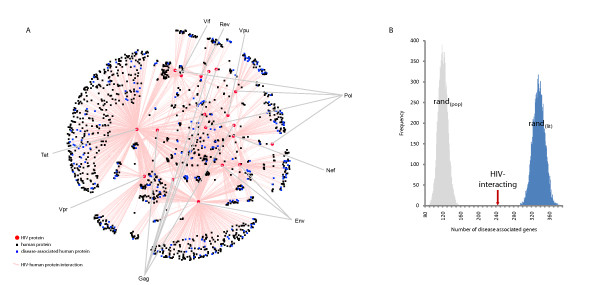
Figure 7.
Disease association and HIV-interacting proteins. (A) Visualisation of disease-associated genes amongst HIV-interacting proteins. Blue squares correspond to human proteins identified in OMIM as being disease-associated. Black squares and red circles correspond to human and HIV proteins, respectively. Pink edges correspond to interactions between HIV-1 and human proteins, as shown in Figure 4. HIV proteins are labelled accordingly. (B) Number of disease associated genes amongst HIV and randomised data sets. Without correcting for bias, rand(pop)contained an average 120 (8.39%) disease-associated genes, compared to 244 (17.05%) disease-associated genes in the HIV set (p-value of 8.58 × 10-32). When the bias is corrected for, rand(lit)contains an average 336 (23.48%) disease-associated genes, which is different to the HIV-1 interacting sample (p-value of 3.48 × 10-12).