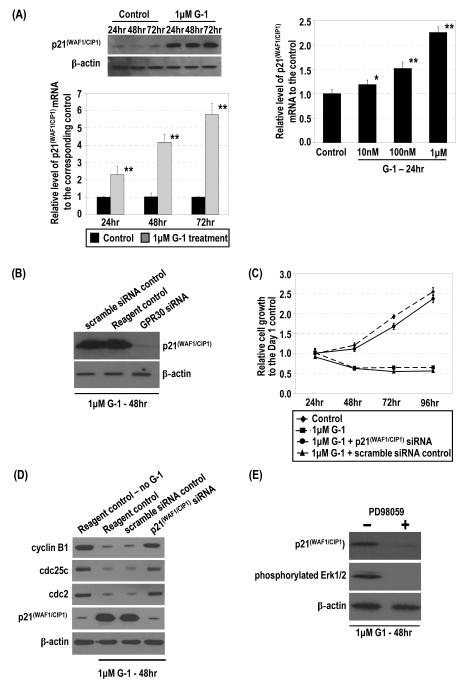
Figure 4.
G-1 induced p21 mRNA and protein via GPR30 and downregulation of expression of G2 checkpoint regulators for inhibition of cell growth by p21. (A) PC-3 cells were treated with 1 μM G-1 or ethanol. Levels of p21 protein and mRNA were determined by Western blot and real-time RT-PCR analyses, respectively. Furthermore, the cells were treated with 10−8–10−6 M G-1. Levels of p21 mRNA in cells were quantified by real-time RT-PCR analysis. *, p<0.01; **, p<0.001. (B) The siRNA-treated cells (GPR30siRNA) and controls (scramble siRNA control and reagent control), all treated with 1 μM G-1, were lysed and the levels of p21 and β-actin protein determined by Western blot analysis. (C) The G-1–treated cells with p21 siRNA or the scramble siRNA control were subjected to Western blot analysis to determine levels of cyclin B1, cdc25c, cdc2, p21, and β-actin protein. Two reagent controls (ethanol or 1 μM G-1) were included. (D) Effects of p21siRNA knockdown on the G-1–induced inhibition of cell growth are presented with the controls. Growths of the cells relative to that of the ethanol control at day 1 were determined. (E) G-1–induced expression of p21 was dependent on Erk1/2 activation. PC-3 cells were treated with 1 μM G-1 for 48 h in the presence or absence of 30 μM PD98059. The levels of p21 and β-actin protein were determined by Western blot analysis.