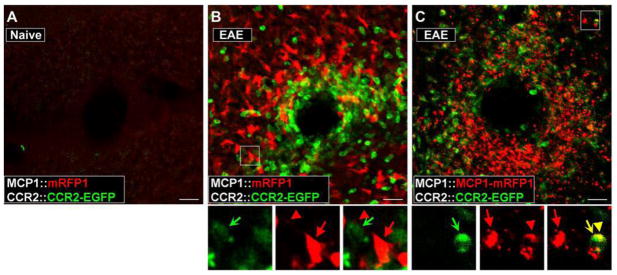
Figure 2.
Activation of CCR2 receptors in peripheral leukocytes during the pathogenesis of EAE can be visualized in the BAC transgenic mice. EAE was induced in MCP1:mRFP1; CCR2::CCR2–EGFP mice (B) and MCP1::MCP1-mRFP1; CCR2::CCR2-EGFP mice (C). The pictures were taken from the white matter from coronal cerebellar sections. Unlike control conditions (A), there was a marked infiltration of leukocytes (B, C; CCR2-EGFP+) into the parenchyma of the cerebellum (examined on postoperative day 14). Magnified views of the boxed areas are shown below B and C. Although there were close interactions between MCP1 (red arrow, cell body; red arrowhead, cellular process)- and CCR2-expressing cells (green concave arrow) (B, C), onlyMCP1–mRFP1(C), but not mRFP1 alone (B), was transferred to CCR2–EGFP-expressing leukocytes as indicated from the appearance of yellow internal vesicles (yellow arrow and arrowhead). Scale bars, 20μm. Courtesy of the Society for Neuroscience.