Figure 1. CA1 pyramidal neurons in MIA offspring display a reduced frequency and an increased amplitude of mEPSCs, but no significant difference in mIPSCs.
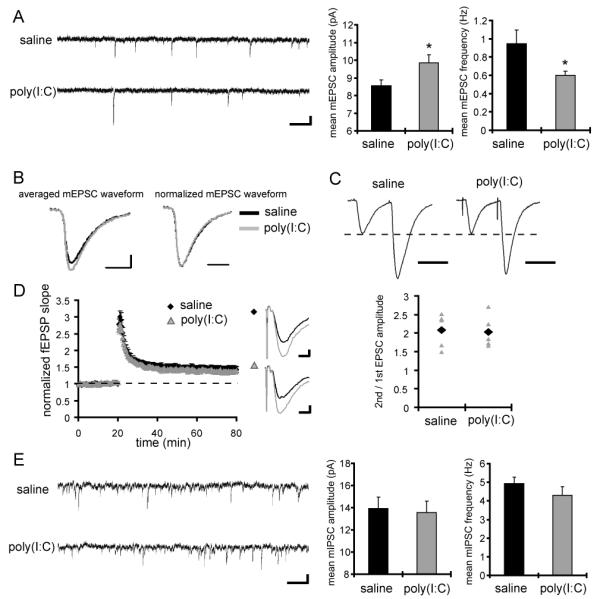
(A) Typical recordings and quantification of mEPSCs from CA1 pyramidal neurons are shown (saline: n = 11 neurons, poly(I:C): n = 12 neurons, 4 pairs of animals) (scale bar = 500 ms, 10 pA) (*p < 0.05 relative to control). (B) Averaged mEPSC waveforms from animals used for the analysis in A are shown on the left. The mEPSC waveform in MIA offspring shows larger amplitude compared to that in control animals. To examine the kinetics of the waveforms, the amplitudes of mEPSC waveforms are normalized on the right. There is no significant difference in kinetics of mEPSCs between the groups. (C) Whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings were performed in CA1 pyramidal neurons under inhibitory blockade with the GABA receptor antagonists bicuculline (10 μM) and CGP55845 (1 μM). Membrane potential was clamped at −60 mV. Paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) was analyzed at Schaffer-collateral-CA1 synapses. The left panel shows representative waveforms (interstimulus interval is 50 ms; scale bar = 50 ms), and the right panel shows the PPF ratio (2nd/1st EPSC amplitude) of individual recordings (gray triangles), and the mean values (black diamonds) (n = 5 neurons for each group, 3 pairs of animals). (D) Extracellular field recordings were performed at Schaffer-collateral-CA1 synapses under fast inhibitory transmission block with the GABAA receptor antagonist bicuculline. The left panel shows the normalized fEPSP slope from control animals (black diamonds) and MIA offspring (gray triangles) and LTP was induced at 20 min by a single train of 100 stimuli at 100 Hz. The right panel shows representative waveforms before (black) and after (gray) LTP induction (scale bar = 0.2 mV, 5 ms). No significant difference is observed in LTP magnitude between animal groups (n = 8 slices for each group, 3 pairs of animals). (E) Typical recordings and quantification of mIPSCs from CA1 pyramidal neurons are shown (n = 12 neurons for each group, 3 pairs of animals). A cesium chloride-based solution was used as the internal solution of patch pipettes and recordings were made at 28 °C in the presence of TTX (1 μM), NBQX (20 μM) and APV (50 μM) to block excitatory synaptic transmission. The extracellular potassium concentration was increased from 2.5 mM to 5 mM to enhance the frequency of miniature synaptic events. No significant difference is observed in mIPSC amplitude or frequency between the groups.
