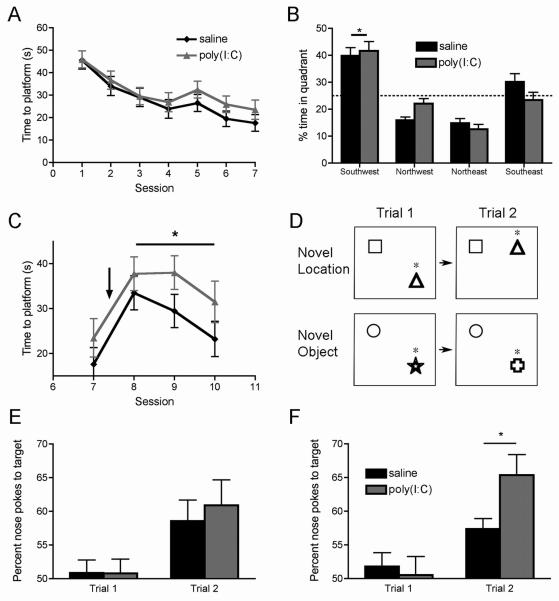
Figure 5. The offspring of poly(I:C)-treated mothers display behavioral inflexibility in platform relocation in the Morris water maze task, and abnormal preference in the novel object recognition task.
(A) In the Morris water maze, the latency to find the platform is similar in the MIA offspring compared to controls (saline: n = 16, poly(I:C): n= 17). (B) Both control and MIA offspring show a significant learned preference for the target quadrant in the session 7 probe trial, which was not present before training (*p < 0.05 vs. all other quadrants). (C) When the location of the platform was moved after training (indicated by arrow), the MIA offspring do not learn the new location as quickly as controls (*p < 0.05). The experimental groups diverge significantly after the platform is moved, at the point indicated by the arrow. (D) A graphical representation of the object location and novel object recognition tests illustrates how the location of the target object, or the type of target object itself, is changed in the 5 min interval between trial 1 and 2. Asterisks indicate the target objects. (E) In the novel location test, both control and MIA offspring show a significant preference for the target object in trial 2, compared to trial 1 (p < 0.05), but there is no difference between control and MIA offspring. (F) In the novel object recognition test, both groups also display a significant preference for the target object in trial 2 compared to trial 1 (p < 0.05). Moreover, compared to control animals, the MIA offspring show a significantly greater preference for the target object in trial 2 (n = 16 animals per group) (*p < 0.05).