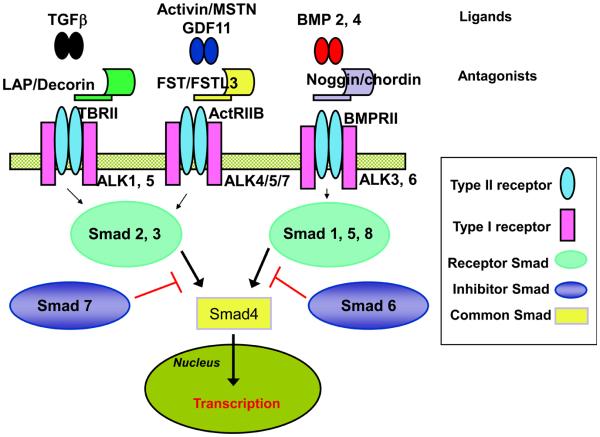
Figure 2.
TGFβ family ligands and signaling pathways reported in islets. TGFβ family ligands representing members of both TGFβ/activin and BMP subfamilies that have been identified in islets are shown with their receptors, soluble inhibitors, second messengers, and inhibitory Smads. Whereas this family is known for promiscuity in receptor usage owing to the more than 40 members sharing 5 Type II and 7 Type I receptors, there are also differences within the subfamilies that allow some degree of specificity when analyzing genetic alterations in mouse models. For example, Smad7 overexpression inhibits all members of the TGFβ/activin subfamily but usually not members of the BMP subfamily. Follistatin and FSTL3 inhibit members of the activin branch of the TGFβ/activin subfamily but not TGFβ itself. Noggin inhibits BMP ligands but not activin or TGFβ. Despite these mouse models, the actions of individual ligands in regulating β-cell function and glucose homeostasis remain to be elucidated. Adapted from [4] with permission.