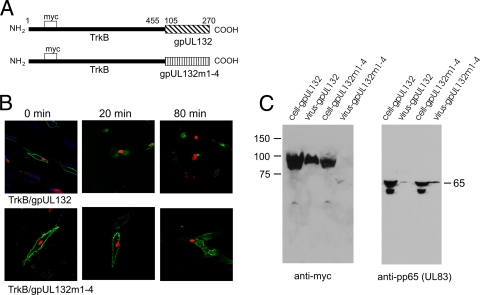
FIG. 9.
Trafficking and virion incorporation of a TrkB/gpUL132 chimeric protein. (A) Cartoon illustrating the domains of the chimeric proteins. (B) Antibody internalization endocytosis assay of chimeric forms of TrkB molecules. HF cells, grown on 13-mm coverslips, were electroporated with the respective chimeric proteins as described in the text and infected with HCMV. On day 5 postinfection, cells were cooled to 4°C and incubated with an anti-myc MAb for 2 h. The cell cultures were then washed several times with warm medium, and individual coverslips were harvested at the indicated time points. After fixation in paraformaldehyde, the coverslips were reacted with an anti-IE1 MAb to identify infected cells and then developed with FITC-conjugated anti-mouse IgG1 (green) to detect internalized anti-myc antibodies and with TRITC-conjugated anti-mouse IgG2b (red) to detect anti-IE1 antibodies. (C) Virion incorporation of the TrkB/gpUL132 chimeric proteins. HF cells were electroporated with expression plasmids encoding the respective chimeric protein and then infected with HCMV 24 h later. Cells were harvested, and supernatant virus was collected by centrifugation. Viral proteins were solubilized and analyzed by immunoblotting using an anti-myc MAb to detect the chimeric protein and an anti-pp65 MAb to detect viral pp65.