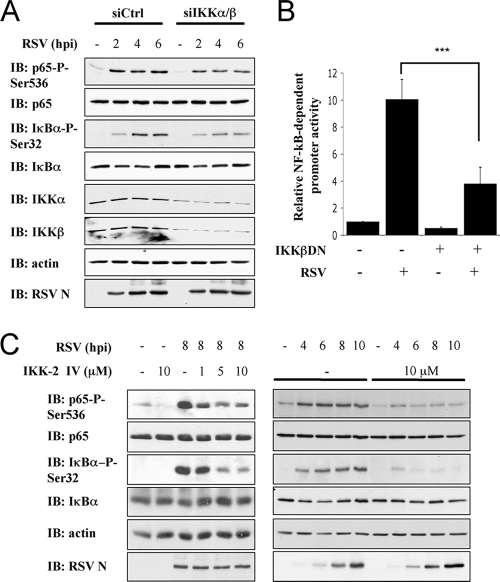
FIG. 5.
Phosphorylation of p65Ser536 during RSV infection is mediated by IKKβ. (A) A549 were transfected with control (Ctrl)- and a combination of IKKα- and IKKβ-specific siRNA (Table 1). siRNA-transfected A549 were further infected with RSV (MOI = 3) for the indicated times (hpi). WCE were resolved by SDS-PAGE and revealed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-IκBαSer32 phospho-specific (IκBα-P-Ser32), anti-IκBα, anti-p65Ser536 phospho-specific (p65-P-Ser536), anti-p65, anti-RSV (nucleocapsid protein [N] is shown), anti-IKKα, anti-IKKβ, and anti-actin antibodies. The immunoblots are representative of three independent experiments. (B) A549 were cotransfected with the IKKβDN encoding plasmid and the P2(2×)TK-pGL3 NF-κB firefly luciferase and the pRL-null Renilla luciferase (internal control) reporter constructs and either mock or RSV infected. At 8 hpi, luciferase activities were measured and analyzed as described in Fig. 2A. (***, P < 0.001; mean ± the SEM; n = 9.) (C) A549 were pretreated with the IKKβ inhibitor, IKK-2 IV, at the indicated concentrations before being left untreated or infected with RSV at an MOI of 3 for various times (hpi). WCE were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by IB as in panel A. The immunoblots are representative of at least three experiments.