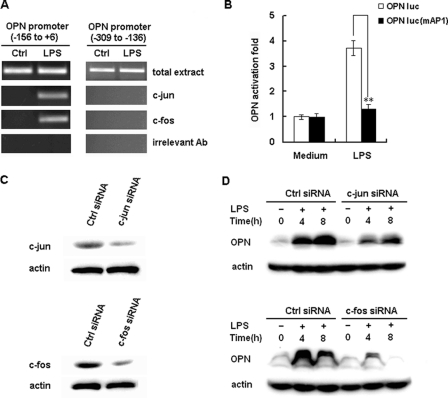
FIGURE 6.
Involvement of AP-1 in LPS-induced OPN expression. A, RAW264.7 macrophages were stimulated with 100 ng/ml LPS or vehicle (water) for 2 h, and the ChIP assay was used to assess the binding of c-Jun and c-Fos to the AP-1 binding sites within the −156 to +6 region of the murine OPN promoter. Total extract was used as a loading control, and immunoprecipitation with irrelevant antibody (anti-actin) was used as a negative control. PCR products from the amplication of an AP-1 site-free region within −309 to −136 of the murine OPN promoter were used as specificity controls. B, RAW264.7 macrophages were transfected with 100 ng of OPN luciferase reporter construct or the AP-1 binding sites mutant reporter construct and 10 ng pTK-Renilla-luciferase plasmid. After 24 h of culture, the cells were stimulated with 100 ng/ml LPS for 6 h. Luciferase activity was measured and normalized by Renilla luciferase activity. Data are shown as mean ± S.D. (n = 6) of one representative experiment (**, p < 0.01). C, RAW264.7 macrophages were transfected with control small RNA (Ctrl siRNA), c-Jun siRNA, or c-Fos siRNA. After 36 h, c-Jun or c-Fos expression in the cells was detected by Western blot. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. D, RAW264.7 macrophages were transfected with Ctrl siRNA, c-Jun siRNA or c-Fos siRNA and then treated with 100 ng/ml LPS for the indicated time period. The production of intracellular OPN was detected by Western blot with R&D OPN Ab. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments.