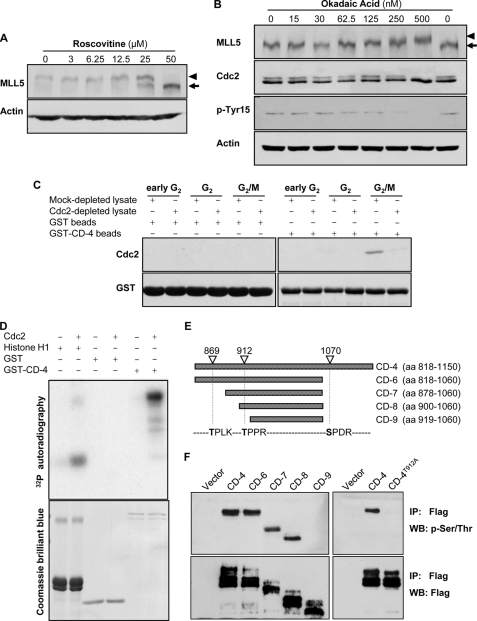
FIGURE 4.
MLL5 is phosphorylated by Cdc2 at G2/M. A, mitotic HeLa cells were treated with various concentrations of roscovitine for 4 h in the presence of nocodazole. The phosphorylation of MLL5 was inhibited by roscovitine in a dose-dependent manner. B, asynchronous HeLa cells were treated with various concentrations of okadaic acid for 4 h. The phosphorylation of MLL5 was gradually induced by okadaic acid in a dose-dependent manner. C, GST-CD-4 protein co-purified with Cdc2 in HeLa cells that were released from the G1/S phase boundary for 12 h (G2/M). D, upper panel, GST-CD-4 was phosphorylated by human recombinant Cdc2-cyclin B1 complex in an in vitro kinase assay. Histone H1 and GST served as a positive and a negative control, respectively. Lower panel, Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining for histone H1, GST, and GST-CD-4. E, schematic representation of MLL5-CD-4 domain and its deletion fragments. The potential Cdc2 targeting sites on MLL5-CD-4 domain are denoted based on the consensus motif for Cdc2 kinase ((S/T)PX(K/R)). aa, amino acids. F, left panel, CD-4 domain and deletion mutants (CD-6–9) with sequential deletion of Cdc2-targeting sites were immunoprecipitated (IP) from nocodazole-synchronized extract of HEK 293T cells using anti-FLAG antibodies and detected by anti-phospho-Ser/Thr or anti-FLAG antibodies. The phosphorylation on MLL5 is abrogated when Thr-912 residue was deleted. Right panel, mutation of Thr-912 to Ala on the CD-4 domain eliminated the phosphorylation modification, suggesting that Thr-912 is the phosphorylation targeting site by Cdc2. WB, Western blot.