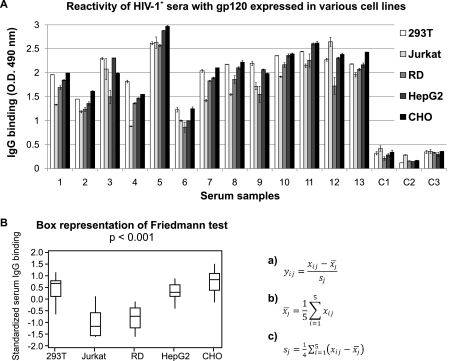
FIGURE 6.
Binding of IgG from HIV-1-positive patients (1–13) and HIV-1 negative control subjects (C1–C3) to purified native recombinant gp120 glycoproteins produced in 293T, HepG2, RD, CHO, and Jurkat cells was tested by ELISA. IgG in serum diluted 1:10,000 was allowed to bind to 96-well plates coated with an equal amount of our recombinant gp120 glycoproteins (0.5 μg/ml) and bound IgG antibodies were detected with anti-human IgG HRP-conjugated antibody. Mean values of absorbance and standard deviations are shown (A). Statistical analysis of differences in binding of serum IgG from HIV-1-positive subjects to individual gp120 preparations was performed by the Friedmann test, with results expressed as a box graph (p < 0.001). For this analysis, ELISA data (serum IgG binding intensity measured by OD) were standardized to eliminate inter-individual differences in absolute gp120-specific IgG concentration. Standardization was performed for values xij, i = 1, …,5, j = 1, …,16 according to the mathematical formula a, where x¯j (with macron) represents mean value for each serum reactivity (with individual gp120 preparations b), and sj is a sample standard deviation of all values measured for each serum c (B).