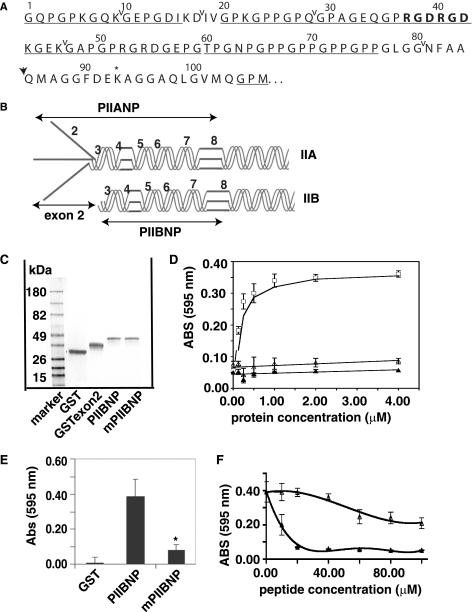
FIGURE 1.
PIIBNP binds to cell surface in an RGD-dependent manner. A, sequence for type IIB NH2-propeptide. ↓, N-proteinase cleavage site; *, cross-link formation site in N-telopeptide. The RGDRGD motif is shown in boldface type, and the GXY sequence is underlined. Carets delineate exons 3–8. B, the type IIA NH2-propeptide (PIIANP) and protein structure contain the eight exons that are represented by numbers, and type IIB NH2-propeptide (PIIBNP) contains seven exons. C, GST fusion proteins were expressed in bacteria and purified as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Protein purity was assayed using a 4–20% SDS-polyacrylamide gel stained with Coomassie Blue. D, 96-well plates were coated with increasing concentrations of GST (▴), recombinant exon 2 (▵), or GST-PIIBNP (□) at 4 °C overnight and blocked with 0.5% bovine serum albumin, and hCh-1 cells were cultured in the plate for the adhesion assay as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The value of absorbance at 595 nm represents the number of cells bound to the proteins. Absorbance values are represented as mean ± S.D. (n = 8). The smooth curves are fitted linear regression or moving average curves. E, RGDRGD motif in PIIBNP was mutated to RADRAD (mPIIBNP). hCh-1 cell adhesion to GST, PIIBNP, and mutant PIIBNP was analyzed as described above. Mutant PIIBNP significantly reduced cell adhesion (*, p < 0.001 compared with PIIBNP, n = 18). F, hCh-1 cells were incubated with either synthetic RGD or RAD peptide at a concentration of 0–100 μm for 15 min at room temperature and then added into the wells for the attachment assay. Absorbance values are represented as mean ± S.D. (n = 8). The smooth curves are fitted moving average curves.