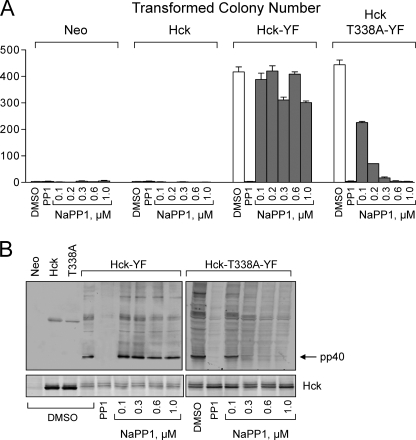
FIGURE 2.
Hck-T338A is biologically active in fibroblasts and selectively sensitive to NaPP1. Rat-2 fibroblasts were infected with recombinant retroviruses carrying a neomycin selection marker (Neo control), wild-type Hck, Hck-T338A, Hck-YF, or Hck-T338A-YF and selected with G418. A, cell populations were plated in triplicate in soft agar in the presence of the indicated concentrations of NaPP1. The general SFK inhibitor and parent compound PP1 (3 μm) was used as a positive control. Transformed colonies were stained with 3-(4,5-dimethyl-thiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide after 10–14 days and enumerated from scanned images using QuantityOne colony-counting software (Bio-Rad). Results from a representative experiment are shown as the mean number of colonies of three plates ±S.D. The statistical significance of Hck expression on colony formation was determined using one-way ANOVA (p < 0.0001) followed by Bonferroni's post test for multiple comparisons (p < 0.001 for Neo versus Hck-YF, Neo versus Hck-T338A-YF, Hck versus Hck-YF, and Hck versus Hck-T338A-YF; p > 0.05 for Neo versus Hck and Hck-YF versus Hck-T338A-YF). The effect of NaPP1 on colony formation by Hck-YF and Hck-T338A-YF cells was assessed using a two-tailed unpaired Student's t test (normal distribution and unequal variance; p < 0.02). The complete experiment was repeated twice with comparable results. B, control or Rat-2 fibroblasts transformed by Hck-YF or Hck-T338A-YF were plated overnight with the indicated concentrations of NaPP1, PP1 (3 μm), or with the vehicle alone (DMSO). Lysates were probed with an anti-phosphotyrosine antibody to determine the phosphorylation status of the endogenous Hck substrate, pp40. Hck expression was confirmed in replicate immunoblots. The entire experiment was repeated twice with comparable results. A representative example is shown.