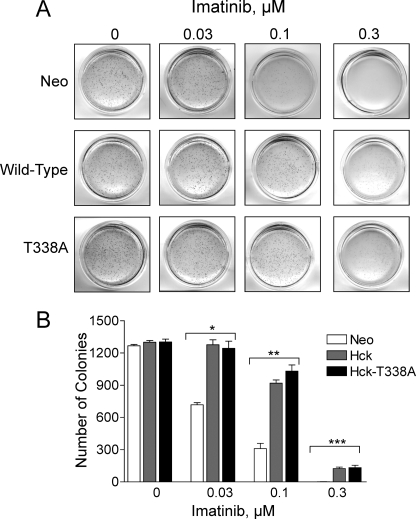
FIGURE 4.
Expression of wild-type Hck or Hck-T338A protects K562 cells from imatinib-induced inhibition of soft-agar colony formation. K562-Neo, K562-Hck, and K562-Hck-T338A cell populations were plated in soft agar colony assays in the presence of the concentrations of imatinib shown. A, colonies were stained 7–10 days later, and representative images of the plates are shown. B, the bar graph shows the average number of colonies from three independent experiments ±S.D. Two-way ANOVA showed significant effects of Hck or Hck-T338A expression (p < 0.0001) and of imatinib treatment (p < 0.0001). One-way ANOVA was performed separately for each concentration of imatinib, across the three groups. The effect of imatinib on colony formation by the three cell lines was statistically significant at 0.03, 0.1, and 0.3 μm (*, p = 0.0003; **, p < 0.0001; ***, p = 0.0015, respectively). Bonferroni's post test for multiple comparisons showed p < 0.001 for Neo versus Hck and Neo versus Hck-T338A at 0.03 and 0.1 μm imatinib and p < 0.01 for Neo versus Hck and Neo versus Hck-T338A at 0.3 μm imatinib.