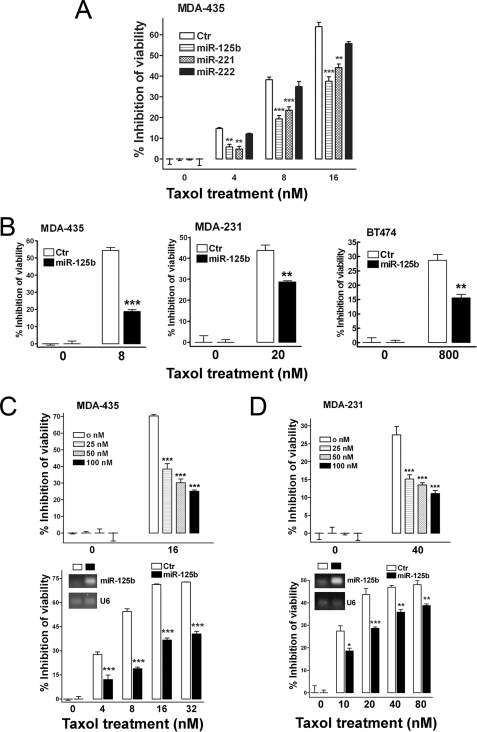
FIGURE 2.
Involvement of miR-125b in Taxol resistance in breast cancer cells. A, MDA-435 cells were transfected with 100 nm pre-miR-negative (Ctr), pre-miR-125b, pre-miR-221, and pre-miR-222. 24 h after transfection, cells were seeded into 96-well plates at the density of 8 × 103 per well. Twelve hours later cells were treated with 0, 4, 8, and 16 nm Taxol for 48 h. Then the cell viability was detected using a MTS reagent. B, breast cancer cells, MDA-435, MDA-231, and BT474, were seeded into 96-well plates 24 h after the transfection of 100 nm pre-miR-125b and then followed with the indicated concentrations of Taxol for 48 h. Pre-miR-negative served as a negative control. The cell viability was detected using MTS reagent. C, MDA-435 cells were transfected with 0, 25, 50, and 100 nm pre-miR-125b (top). Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were seeded into 96-well plates at the density of 8 × 103 cells/well. Twelve hours later cells were treated with 16 nm Taxol for 48 h. Then, the cell viability was detected. MDA-435 cells were transfected with 100 nm pre-miR-negative or pre-miR-125b (bottom). Twenty-four hours after transfection, some of cells were collected for detection of miR-125b level by end-PCR (inset). Some of cells were seeded into 96-well plates at the density of 8 × 103 cells/well. Twelve hours later cells were treated with 0, 4, 8, 16, and 32 nm Taxol for 48 h. Then the cell viability was detected. D, similar experiments were performed in MDA-231 cells as described in panel C. Data are presented as the percentage of viability inhibition measured in cells treated without Taxol. Columns, mean of three independent experiments; bars, S.E. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001.