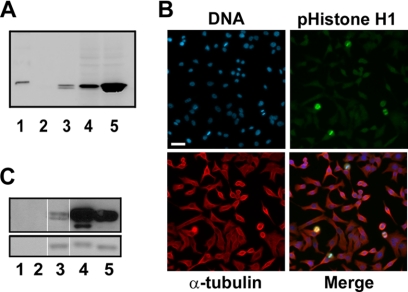
FIGURE 2.
Characterization of a Cdk1-dependent phospho-specific histone H1 (Thr(P)-154) antibody. A, shown is Western analysis of phospho-histone H1 antibody (Thr(P)-154) showing specific cross-reactivity with mitotically phosphorylated histone H1. The loading of the gel was as follows: lane 1, molecular weight marker; lane 2, 1 μg of control unphosphorylated histone H1; lane 3, 1 μg of histone H1 isolated from colcemid-treated HeLa cells; lane 4, 28 μg of protein lysates from CaLu-6 cells; lane 5, 28 μg of protein lysates from CaLu-6 cells treated with nocodazole. B, shown is specific staining of mitotic cells by the phospho-specific histone H1 antibody (Thr(P)-154). Blue = DNA; green = phospho-histone H1; red = α-tubulin. Bar = 60 μm. C, shown is a Western blot analysis of histone H1 in vitro phosphorylated by Cdk1 with the phospho-specific histone H1 antibody (Thr(P)-154). Lanes 1 and 2, Cdk1 kinase alone, from UBI and New England BioLabs, respectively; lane 2, unphosphorylated histone H1 protein control; lanes 4 and 5, histone H1 protein phosphorylated in vitro by Cdk1 kinase from UBI and New England BioLabs, respectively. The upper panel is the Western blot, and the lower panel is Coomassie staining of the gel showing equal loading of histone H1 for Western blot analysis.