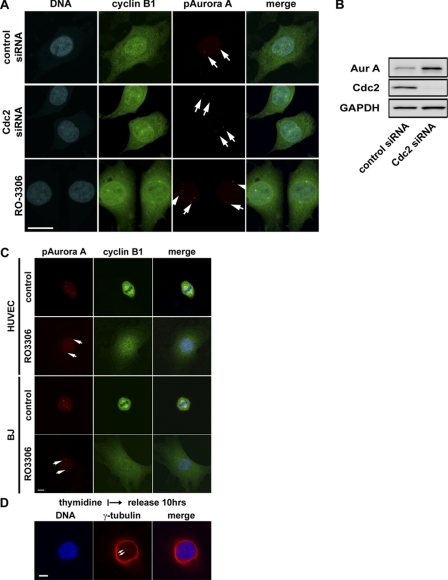
FIGURE 5.
Cdk1-independent activation of Aurora A at centrosomes and centrosome separation at G2. A, representative images of HeLa cells treated with the small molecule Cdk1 inhibitor, RO3306 (9 μm), or Cdk1-specific siRNA and stained for cyclin B1, phospho-specific Aurora A (Thr-288), and DNA are shown. Bar = 20 μm. B, Western blots show effective knockdown of Cdc2 proteins by the Cdc2-specific siRNA oligo. Accumulation of Aurora A (Aur A) kinase in the absence of Cdk1 activity is consistent with G2 cell cycle arrest. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. C, shown are representative images of human umbilical vein endothelial (HUVEC) and BJ cells, non-transformed human cells treated with the Cdk1 kinase inhibitor RO3306 (9 μm) and stained for cyclin B1, and phospho-specific Aurora A (pAurora A; Thr-288) and DNA. Bar = 10 μm. D, shown are representative images of HeLa cells treated with Cdk1 and Aurora kinase inhibitors as indicated and stained for DNA and γ-tubulin. Bar = 10 μm. Cells with inactivated Cdk1 were cleanly arrested at G2. Several hundred cells were examined under the microscope, and all had cytoplasmic cyclin B1 accumulation and activated Aurora A kinase localized to centrosomes which are well separated.