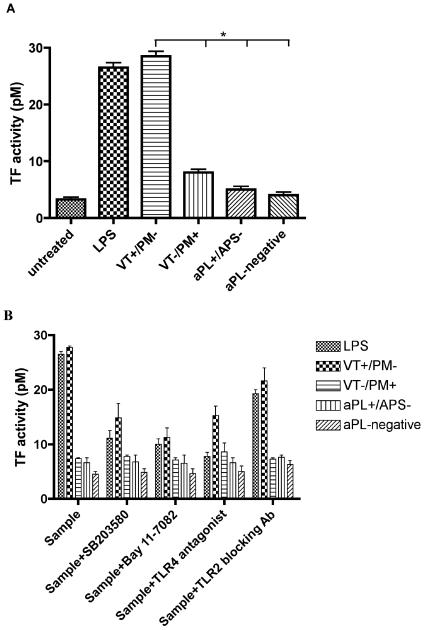
Figure 5. APS-IgG activates monocyte TF activity.
(A) Only pooled VT+/PM− IgG activates monocyte TF activity. U937 cells were treated with 100μg/ml pooled IgG from four clinical groups (VT+/PM−, VT−/PM+, aPL+/APS− and aPL-negative) or 3μg/ml LPS for 6 hours. Cells were lysed and TF activity (pM) was determined using the Actichrome TF assay. Values represent the mean and standard error of three independent experiments. Statistically significant differences are shown (*p<0.05). (B) APS-IgG activates monocyte TF activity via the NFκB, p38MAPK and TLR4 pathways. U937 cells were pre-treated for 1 hour with 1μM SB203580, 50μM Bay 11-7082, 1μg/ml anti-TLR2 blocking antibody or 1μg/ml TLR4 antagonist (E. coli K12 msbB LPS), then treated with 100μg/ml pooled IgG or 3μg/ml LPS for 6 hours. Cells were lysed and TF activity was measured. Values represent the mean and standard error of two different experiments. The positive control (LPS) confirms that NFκB, p38MAPK and TLR4 pathways were inhibited by addition of the inhibitors.