Fig. 1.
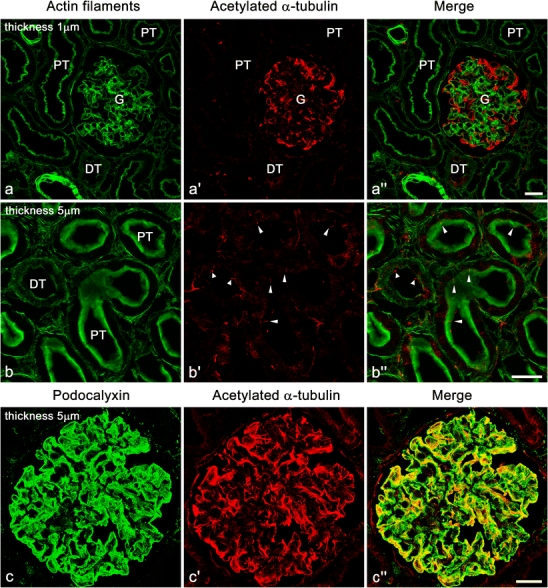
Immunofluorescence labeling for acetylated α-tubulin (Ac-tub, red) in adult rat kidney. a–a″ Strong immunofluorescence signal for Ac-tub is found in the glomerulus (G). Such strong signal is not found in the proximal tubules (PT) and distal tubules (DT). Actin filaments are visualized with FL-phallacidin (green) for identification of glomerulus, tubules, and vasculature. b–b″ In the proximal and distal tubules, the primary cilia (arrowheads) are detected with the anti-Ac-tub antibody at the luminal surface. c–c″ In the glomerulus, immunofluorescence signal for Ac-tub (red) is largely colocalized with that for podocalyxin (green), which is predominantly localized at the apical surface membrane of podocytes. It is difficult to determine whether or not the mature podocytes of adult rats possess the primary cilia in this staining. b–b″,c–c″ Z-stacked images of 5 µm thickness. Bars 20 µm
