Fig. 1.
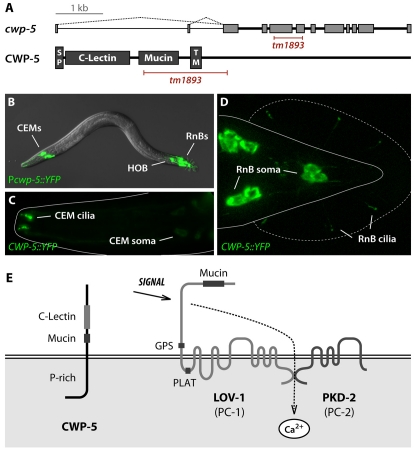
cwp-5 is a novel gene expressed exclusively in male-specific sensory neurons. (A) The cwp-5 gene contains 11 exons and is located at +10.23 cM on the X chromosome. Transcriptome data indicate that cwp-5 has two alternative first exons (indicated with dotted lines) that encode 11 (F48C11.2a) or 14 (F48C11.2b) amino acids. Both CWP-5 products are predicted by SignalP 3.0 (Emanuelsson et al., 2007) to contain functional signal peptides (SP). CWP-5 is also predicted to contain a C-type lectin domain and a mucin-like region, as well as a single-pass transmembrane (TM) domain. The allele tm1893 is an in-frame insertion-deletion removing most of the mucin domain and the entire transmembrane domain to yield a truncated, potentially secreted, protein. The predicted structure of the mutant transcript was confirmed by sequencing the cwp-5(tm1893) cDNA. (B) Expression of a transcriptional cwp-5::YFP reporter using the upstream (F48C11.2b) promoter was observed in 21 male-specific sensory neurons: 4 CEM neurons in the head, 16 RnB-type ray neurons (all RnBs except for those of ray 6), and the hook neuron HOB. A translational reporter, CWP-5::YFP, in which the YFP sequence was inserted at the 3× end of cwp-5, should reflect both isoforms of CWP-5. This construct marked the same set of cells, with fluorescence visible in the cell bodies, dendrites and the cilia of CEM (C), RnB (D) and HOB (not shown) neurons. The cilia in the CEM and RnB neurons are roughly 4 and 1 μm in length, respectively. (E) A model for the membrane topology of CWP-5 and the polycystins in sensory cilia. Domains of each of these proteins are noted. As shown here, signaling through the polycystin complex is thought to be mediated by regulated Ca2+ entry.