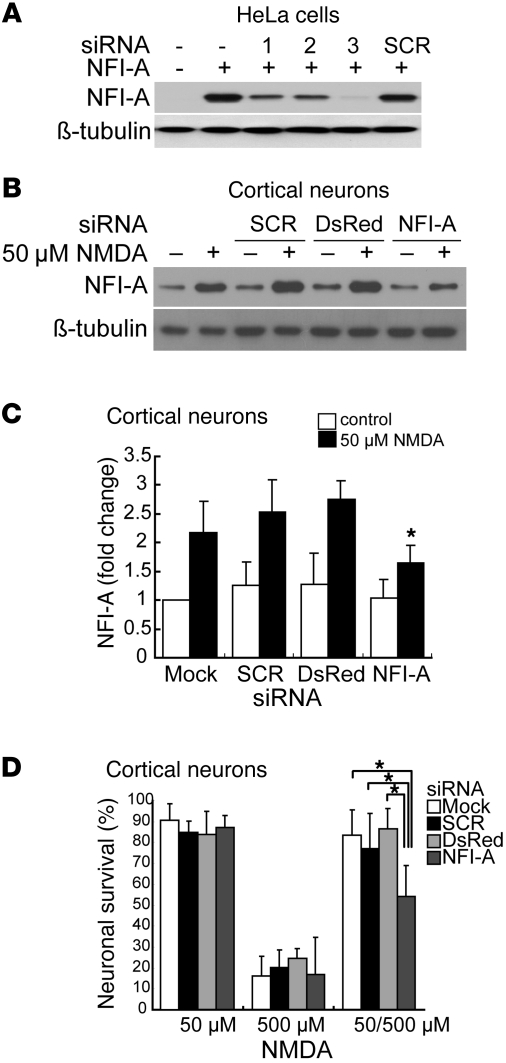
Figure 2. Blocking NFI-A induction by 50 μM NMDA neuroprotective treatment significantly inhibits its protective effects.
(A) Knockdown of ectopic NFI-A expression by NFI-A siRNAs (1, 2, and 3) in HeLa cells. SCR, scrambled control siRNA. siRNA and NFI-A expression plasmid were cotransfected into HeLa cells. Twenty-four hours after transfection, NFI-A expression levels were examined from total cell lysates. These experiments were replicated 3 times. (B) Immunoblot analysis of blockade of NFI-A induction by 50 μM NMDA treatment using NFI-A siRNA 3, but not by SCR siRNA or DsRed siRNA molecules. Cortical cultures were transfected with siRNA 1 day and 3 days prior to 50 μM NMDA treatment and were harvested 24 hours after NMDA treatment. Experiments were replicated 3 times. (C) Quantification of NFI-A levels. *P < 0.01, 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer post-hoc test. (D) Neuronal viability after 500 μM NMDA excitotoxicity in cortical cultures. siRNAs were transfected twice at 3 days and 1 day prior to 50 μM NMDA treatment. The cultures were challenged with 500 μM NMDA toxicity for 5 minutes at 24 hours after the 5-minute 50 μM NMDA treatment. Experiments were replicated at least 3 times, with at least 6,000 neurons counted per experiment. NFI-A siRNA treatment (right gray bar) significantly blocks the protective effects of 50 μM NMDA against 500 μM NMDA treatment. *P < 0.01, 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer post-hoc test.