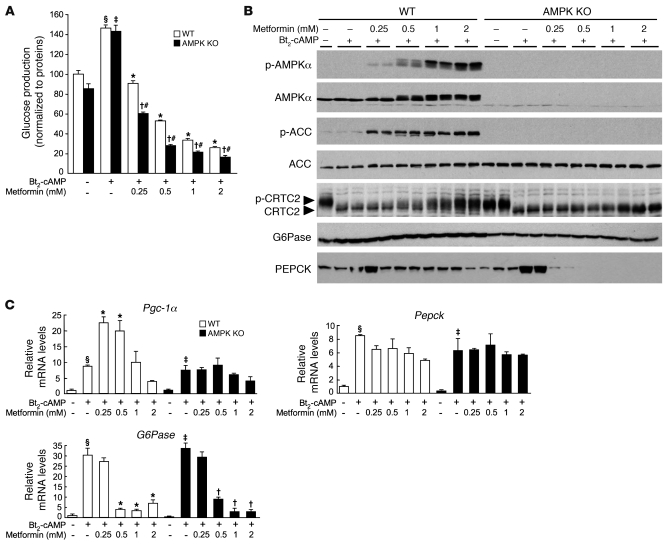
Figure 1. Metformin inhibits gluconeogenesis in AMPKα1α2-null (AMPK KO) mouse hepatocytes.
After attachment, WT and AMPK-deficient primary hepatocytes were cultured for 16 hours in M199 medium containing 100 nM dex. Hepatocytes were then incubated in glucose-free DMEM containing lactate/pyruvate (10:1 mM) and 100 nM dex alone or with 100 μM Bt2-cAMP and with or without 0.25, 0.5, 1, or 2 mM metformin. After 8 hours, medium was collected for glucose measurement and cells were harvested for Western blot and gluconeogenic gene expression analyses. (A) Glucose production was normalized to protein content and presented as a percentage of glucose produced by WT hepatocytes incubated in the absence of both Bt2-cAMP and metformin. Results are representative of 5 independent experiments. (B) Immunoblots were performed against phospho-AMPKα (Thr172), AMPKα, phospho-ACC (Ser79), ACC, CRTC2, G6Pase, and PEPCK. Blots are representative of at least 5 independent experiments. (C) Relative mRNA levels of Pgc-1α, Pepck, and G6Pase expressed as fold activation relative to levels in WT hepatocytes incubated in the absence of both Bt2-cAMP and metformin. Results are representative of 5 independent experiments. Data are mean ± SEM. §P < 0.001, ‡P < 0.001 compared with WT and AMPK-KO hepatocytes incubated without Bt2-cAMP; *P < 0.001, †P < 0.001 compared with WT and AMPK-KO hepatocytes incubated with Bt2-cAMP alone; #P < 0.01 compared with WT hepatocytes incubated under the same conditions.