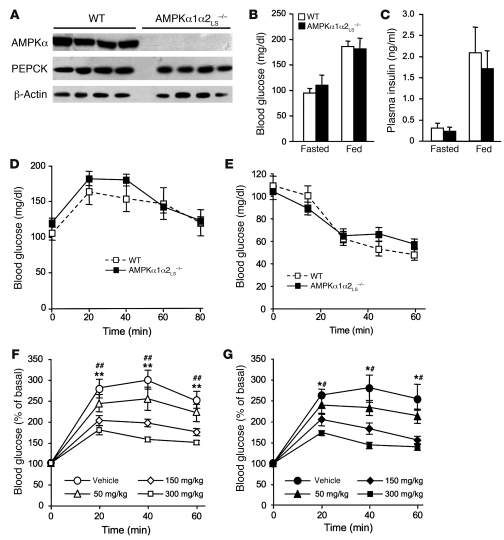
Figure 2. Effects of metformin on blood glucose levels in AMPKα1α2LS–/– mice.
(A) Western blot analysis of AMPKα and PEPCK proteins in livers from 24-hour-fasted control and AMPKα1α2LS–/– mice. β-Actin was immunoblotted as a loading control. Each lane represents the liver sample from an individual mouse. (B) Plasma blood glucose levels were measured in fasted and fed control and AMPKα1α2LS–/– mice. n = 5–6. (C) Plasma insulin levels were measured in fasted and fed control and AMPKα1α2LS–/– mice. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 5–6). (D) Pyruvate tolerance tests (2 g/kg) in control and AMPKα1α2LS–/– mice were used to assess hepatic gluconeogenesis. n = 6–7. (E) Insulin tolerance tests (0.25 U/kg) in control and AMPKα1α2LS–/– mice. n = 6–9. Metformin tolerance tests in control (F) and AMPKα1α2LS–/– (G) mice. Mice were given an oral gavage dose of 50, 150, or 300 mg/kg metformin or vehicle and after 30 minutes challenged with an oral administration of glucose (3 g/kg body weight). n = 6–10. Data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, 150 mg/kg metformin compared with vehicle control; #P < 0.01, ##P < 0.001, 300 mg/kg compared with the vehicle control.