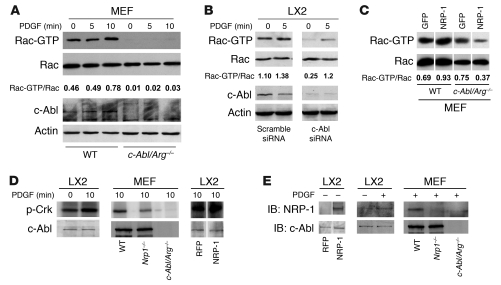
Figure 7. NRP-1 promotes Rac1 activity through c-Abl kinase activity.
(A) Rac activity assay of c-Abl/Arg–/– MEFs was performed using GST-PBD pulldown assay after administration of PDGF (10 ng/ml) at different time points (0–10 minutes). Each group was analyzed by Western blot using Rac1 Ab. c-Abl/Arg–/– MEFs displayed impaired Rac1 activity. (B) siRNA knockdown of c-Abl was examined in LX2 cells incubated with vehicle or PDGF (10 ng/ml) for 5 minutes. Rac activity assay was performed from cell lysates and revealed reduced activity in cells transfected with c-Abl siRNA. Total Rac, c-Abl, and actin blots were performed on parallel, identically loaded membranes at the same time as GST pulldowns or autoradiography. (C) NRP-1 was overexpressed in wild-type or c-Abl/Arg–/– MEFs, and Rac1 activity was measured. Rac activity was markedly diminished in c-Abl/Arg–/– MEFs despite NRP-1 overexpression. (D) LX2 cells or MEFs (wild-type, Nrp1–/–, c-Abl/Arg–/–) were assessed for c-Abl activity in the presence or absence of PDGF. PDGF stimulation increased c-Abl activity in LX2 cells (left panel), and PDGF-induced c-Abl activity was impaired in MEFs isolated from Nrp1–/– MEFs (middle panel). Overexpression of NRP-1 enhanced c-Abl activity in the presence of PDGF (right panel). (E) Association of c-Abl and NRP-1 was assessed by coimmnuoprecipitation assay using c-Abl Ab. Binding of c-Abl and NRP-1 was enhanced in LX2 cells overexpressing NRP-1 (left panel). PDGF promoted binding of c-Abl and NRP-1 (middle panel). PDGF-induced binding was not detected in MEFs isolated from c-Abl/Arg–/– or Nrp1–/– MEFs (right panel). (C–E) Samples were run on the same membrane; noncontiguous lanes are denoted by white lines.