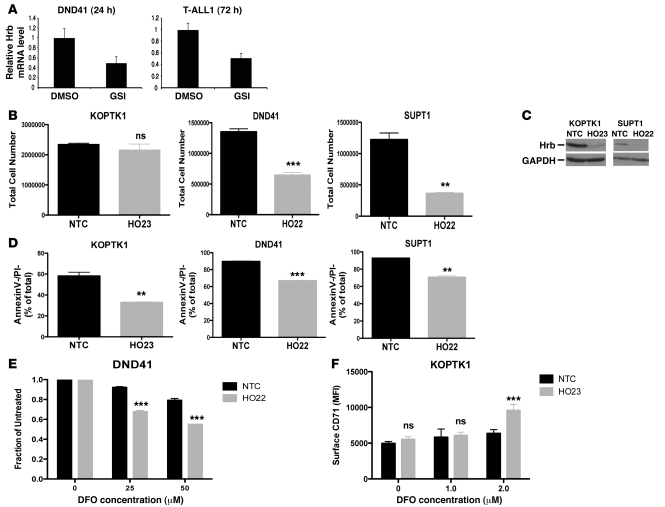
Figure 8. Hrb is regulated by Notch signaling in human T-ALL cell lines and is required for cell proliferation and survival.
(A) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis demonstrating the downregulation of Hrb following treatment with GSI (1 μM). Human T-ALL cell lines DND41 and T-ALL1 were treated with DMSO or GSI for 24 hours and 72 hours, respectively. Total RNA was prepared for reverse transcription and human Hrb mRNA abundance was measured by quantitative RT-PCR. (B) Nontarget control (NTC) and Hrb knockdown (HO22/HO23) stably transduced T-ALL cell lines were seeded at 100,000 cells/well and cultured for 7 days. Total cell numbers were counted based on forward and side scatter. (C) Western blot of lysates prepared from KOPTK1 and SUPT1 cell lines stably transduced with nontarget control and HO22/HO23 Hrb knockdown lentiviral vectors. Membranes were blotted with Hrb (clone H-300) and GAPDH (loading control). (D) Nontarget control and Hrb knockdown (HO22/HO23) stably-transduced T-ALL cell lines were seeded at 100,000 cells/well and cultured for 7 days. Cell survival was assessed using annexin V/PI staining. (E) DFO sensitivity of DND41 cells stably transduced with nontarget control or HO22. nontarget control or HO22 DND41 T-ALL cells were treated with 0, 25, or 50 μM DFO for 4 days. Following treatment, total cell numbers were acquired based on forward/side scatter and normalized to untreated. (F) Surface CD71 levels on NTC and HO23 stably transduced KOPTK1 cells treated with 0, 1.0, and 2.0 μM DFO. Data are shown as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.