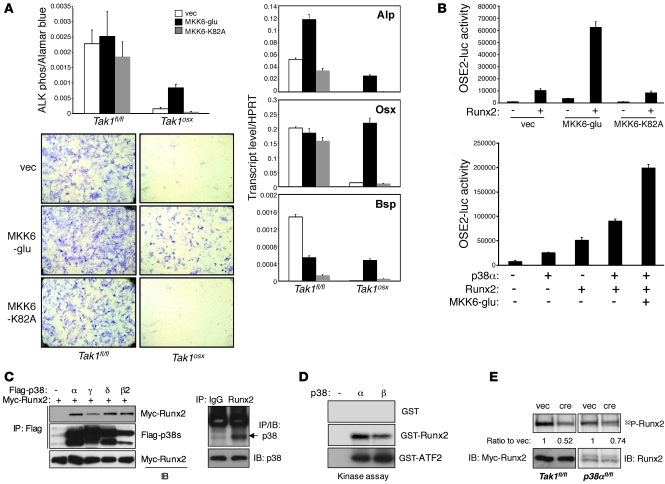
Figure 7. TAK1-mediated p38 MAPK pathway regulates Runx2 activity.
(A) Tak1fl/fl and Tak1osx CalvOb were infected by vector or Flag-tagged MKK6-glu– or MKK6-K82A–expressing lentiviruses, and ALP activity was analyzed by colorimetric assay and Fast Blue staining (left). Alternatively, total RNAs were extracted for quantitative PCR analysis (right). Original magnification, ×25. Values are mean + SD. (B) C2H10T1/2 cells were transfected with OSE2-luc and Renilla luciferase vectors together with either vector, MKK6-glu, or MKK6-K82A in the absence or the presence of Runx2 (left) or various combinations of Runx2, p38α, and MKK6 (right). Results are expressed as relative luciferase activity normalized by Renilla control. Values are mean + SD. (C) The interaction of p38 MAPKs with Runx2. HEK293 cells were transfected with Myc-Runx2 together with Flag-p38 proteins. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag–conjugated beads and immunoblotted with anti-Myc antibody (left). Alternatively, immortalized osteoblasts were immunoprecipitated with either IgG or anti-Runx2 antibody and protein A agarose and immunoblotted with anti-p38 antibody (right). (D) p38-induced phosphorylation of Runx2. Recombinant p38α and p38β proteins were mixed with GST, GST-Runx2, or GST-ATF2 protein, and p38 kinase activity was analyzed by in vitro kinase assay. (E) Primary p38afl/fl CalvOb were infected with either vector or cre lentivirus (left), and Tak1fl/fl CalvOb were infected with either vector or cre lentivirus together with Myc-Runx2–expressing lentivirus (right), metabolically labeled with (P32) orthophosphate, and then immunoprecipitated with either anti-Myc antibody (left) or anti-Runx2 antibody (right). Expression of Myc-Runx2 and Runx2 protein was analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies specific to Myc and Runx2.