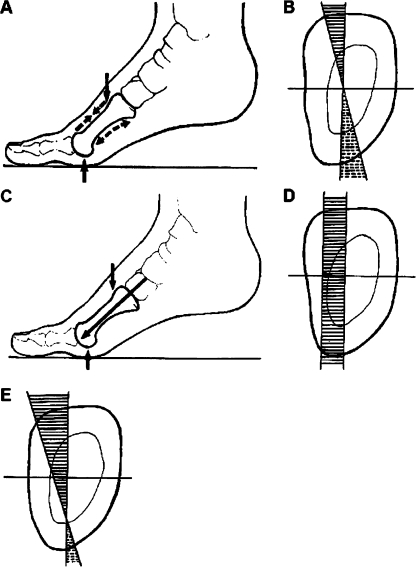
Fig. 4.
Schematic representation of pressure and tension forces acting on the metatarsal diaphysis. The upper panel illustrates a balance between pressure and tension. aDashed arrows represent the direction of the pressure forces along the dorsal surface and direction of the tension forces along the plantar surface. b Pressure and tension in a coordinate system originating from the diaphysis centre (axial cross section)—forces are the greatest on the bone surfaces and decay towards the origin (mutual neutralisation) where the force is zero. The middle panel illustrates isolated pressure forces. c Direction along the metatarsal axis. d In a coordinate system—when there is no counteracting tension—pressure is not neutralised throughout the diaphysis. The lower panel (e) illustrates an imbalance between pressure and tension—the “zero force” point is displaced towards the plantar surface, tension forces on the plantar surface are weaker than in a balanced state, whereas pressure forces on the dorsal surface are greater than in a balanced state