Fig. 1.
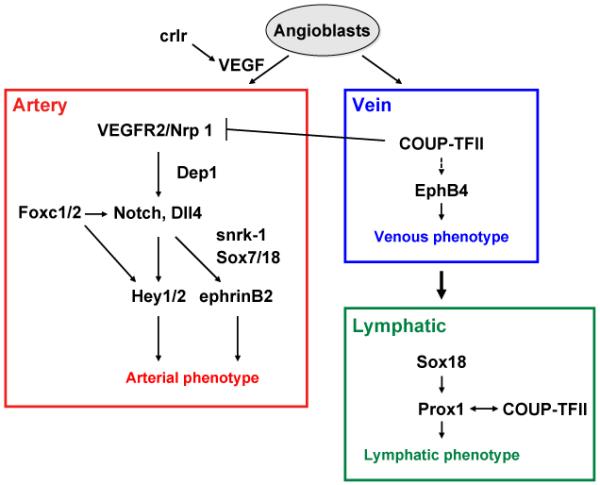
A model for molecular pathway for arterial, venous and lymphatic cell fate determination in vertebrate embryo. The VEGF-VEGFR2/Nrp1 pathway activates Notch signaling in angioblasts, leading to the specification of arterial cell fate, while crlr controls VEGF expression. Dep1 acts upstream of the VEGF-activated PI3K pathway. Foxc1 and Foxc2 directly regulate Dll4 and Hey2 expression, presumably downstream of VEGF signaling. Sox7/18 and snrk-1 may act upstream of grl (the Hey2 homolog in zebrafish). EphrinB2 is a downstream target of Notch. In venous endothelial progenitors, COUP-TFII suppresses Nrp1 and Notch activation and promotes venous cell fate. A subpopulation of venous endothelial cells subsequently expresses Sox18 and Prox1, thereby inducing lymphatic cell fate. COUP-TFII also contributes to lymphatic gene expression by interacting with Prox1.
