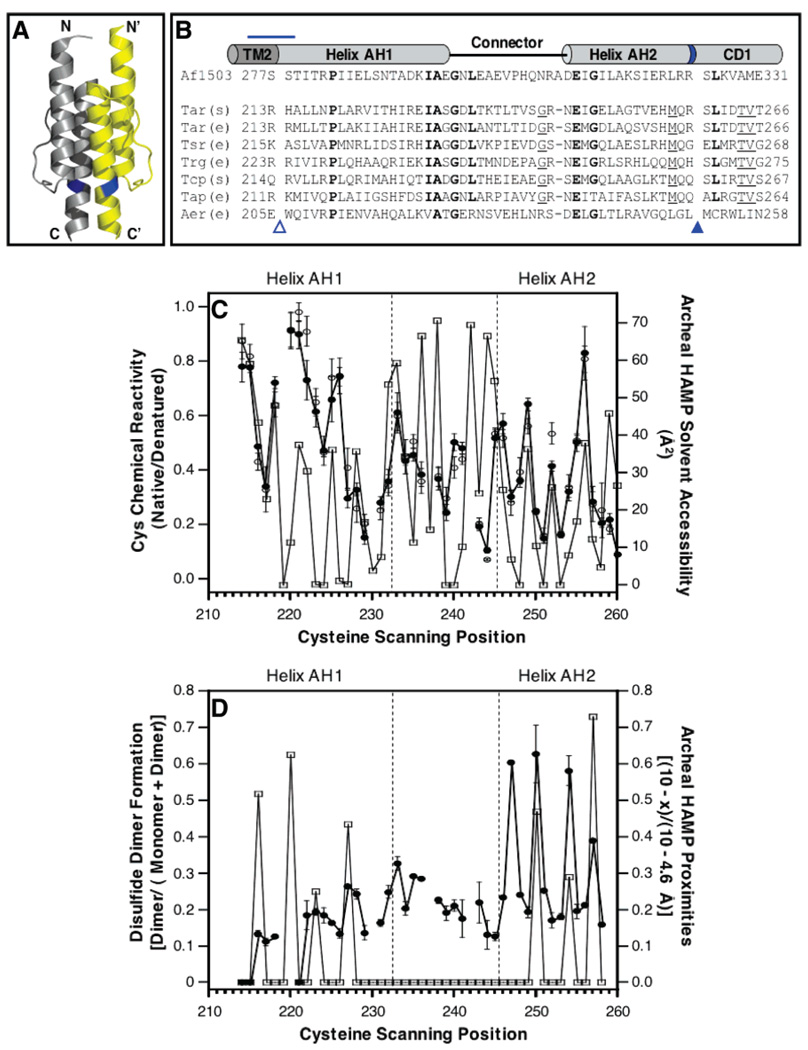
Figure 1.
Previous studies of the conserved HAMP motif. (A) Recent NMR structure of a HAMP domain isolated from an archeal transmembrane protein of unknown function (6), illustrating in cartoon form the parallel, four-helix bundle architecture generated by the association of two identical subunits (yellow and gray) in a symmetric homodimer. (B) Sequence alignment of representative HAMP domains (5, 6), indicating their putative helix–loop–helix regions. Bold residues are most widely conserved in these sequences; underlined residues are conserved except in the archeal and Aer sequences. The blue horizontal line highlights a change of helix register in the aspartate receptor (4); the empty triangle indicates the location of the membrane–water interface (4); and blue band and filled triangle denote the location of an arginine side chain, conserved in some but not all receptors, which is the major site of proteolysis in the S. typhimurium aspartate receptor (25). The latter position may represent the border between HAMP amphiphilic helix 2 (AH2) and cytoplasmic domain helix 1 (CD1) (see the text). (C) Comparison of cysteine chemical reactivities, previously measured for the aspartate receptor HAMP [thick line, ●, (−) Asp; ○, (+) Asp] (4), to the solvent accessibilities calculated for the corresponding positions in the archeal HAMP NMR structure (thin line, □) (6). The correlation is strong in the helical regions, but not in the connector region. (D) Comparison of symmetric disulfide dimer formation, previously measured for the aspartate receptor HAMP (thick line, ●) (4), to spatial proximities calculated for the corresponding cysteine pairs in the archeal HAMP NMR structure (thin line, □) (6). The correlation is strong only in the region of the second helix. Spatial proximities were calculated using the indicated equation where x is the distance in Å between β-carbons.