Figure 16.
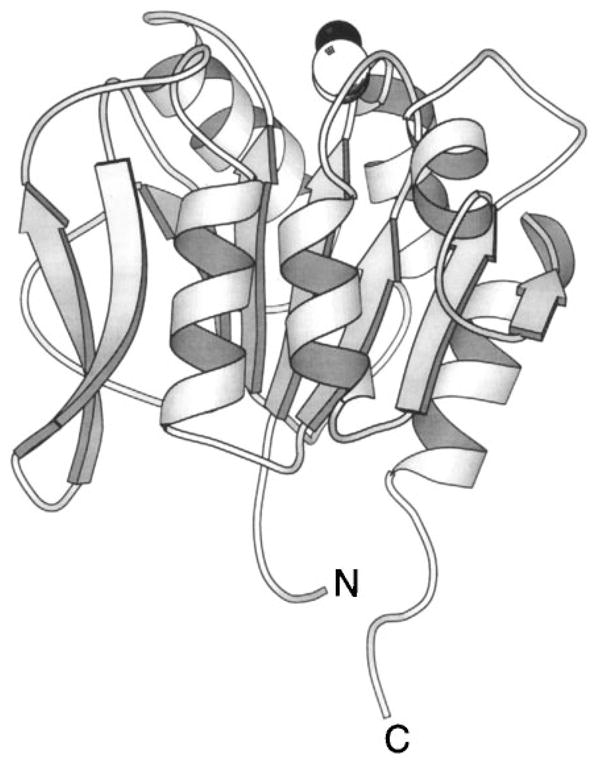
The methylesterase domain of CheB. The C-terminal domain of CheB is a methylesterase that hydrolyzes the regulatory methyl esters and amides of the receptor adaptation sites. In the full-length protein this activity is regulated by phosphorylation of the N-terminal receiver domain (not shown). The crystal structure of the isolated methylesterase domain (West et al 1995) displays an α/β folding motif coupled to a β-hairpin (extreme left). The highlighted Ser164 side chain (CPK, sphere), located on one edge of the β-sheet, acts as the nucleophile in ester and amide hydrolysis.
