Figure 17.
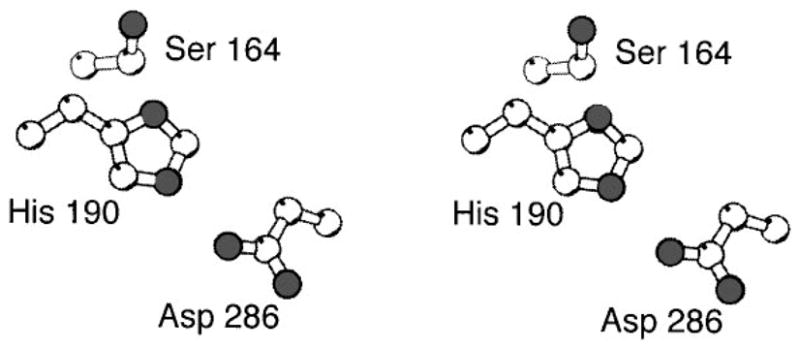
The methyltransferase active site of CheB. Shown are the catalytic residues, including the Ser164 residue essential for catalytic activity and proposed to act as the nucleophile in the methyl ester and amide hydrolysis (West et al 1995). Together the Ser164, His190 and Asp286 side chains form a novel catalytic triad that is functionally, but not structurally, analogous to the catalytic triads of serine proteases.
