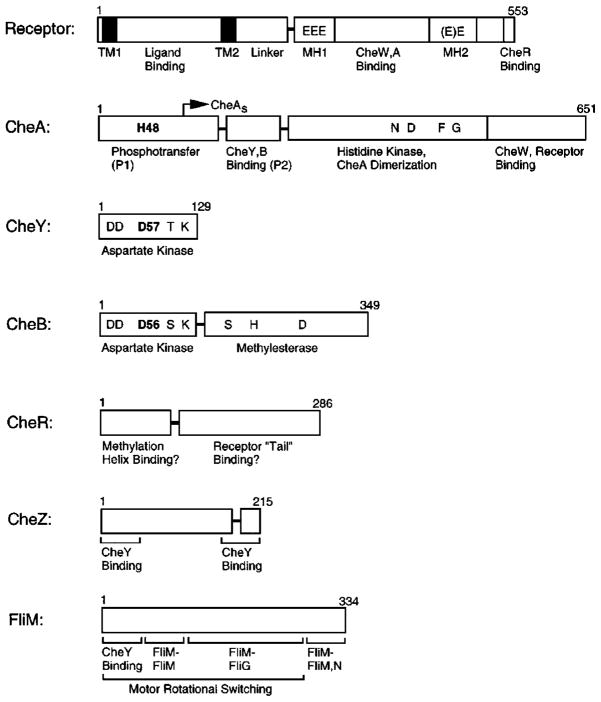
Figure 3.
Domain organization of chemosensory pathway components. Confirmed, proteolytically sensitive interdomain linkers that release stable isolated domains are indicated as horizontal bars; structural or functional subdomains are separated by vertical bars. The aspartate receptor is composed of a sensory ligand-binding and transmembrane-signaling domain, coupled to a cytoplasmic kinase regulation domain (TM, transmembrane; MH, methylation). The transmitter histidine kinase CheA is composed of four functionally distinct domains involved in phosphotransfer (P1), response regulatory docking (P2), dimerization, and histidine autophosphorylation and receptor coupling. CheY and CheB share homologous aspartate kinase receiver domains; CheB also possesses a separate methylesterase domain. Residues shown in bold indicate phosphorylation sites on CheA, CheY, and CheB. Ongoing studies are mapping the domain structures of CheZ and FliM (see text for references).