Figure 7.
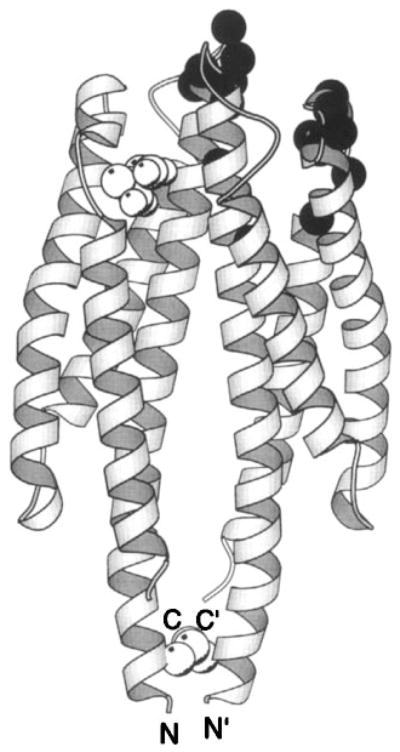
The periplasmic sensory domain of the transmembrane aspartate receptor. The crystal structure of this water-soluble, isolated domain reveals a homodimer of identical four-helix bundles (Milburn et al 1991, Yeh et al 1996). The engineered interdomain disulfide bond (CPK, open sphere, bottom) stabilizes native interactions present in the full-length receptor (Falke & Koshland 1987, Chervitz et al 1995), wherein the membrane-spanning helices would continue in a downward direction. Ligand binding occurs at the opposite, extreme periplasmic end of the domain. Shown is the single molecule of bound aspartate observed in the crystal structure (CPK, open sphere, upper), as well as the genetically defined docking surface for a single molecule of MBP comprised by residues on both receptor subunits (α-carbon, filled sphere; Gardina et al 1997).
