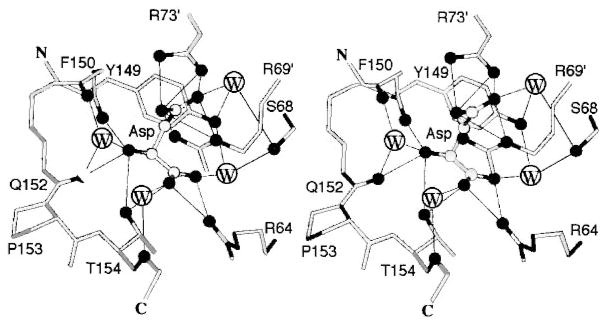
Figure 8.
The aspartate-binding site of the transmembrane aspartate receptor. The dimeric receptor possesses two aspartate-binding sites that are symmetric in the apo dimer. The first molecule of aspartate binds with high affinity to one of these sites, which has been characterized crystallographically as shown (Milburn et al 1991, Yeh et al 1996). Highlighted are the protein residues and four water molecules that provide direct and indirect aspartate coordination, as well as the Ser68 residue implicated in negative cooperativity between the two sites (Kolodziej et al 1996). Owing to this negative cooperativity, the first aspartate binding event substantially weakens or completely prevents the second binding event (Biemann & Koshland 1994, Danielson et al 1994, Yeh et al 1996).