Fig. 3.
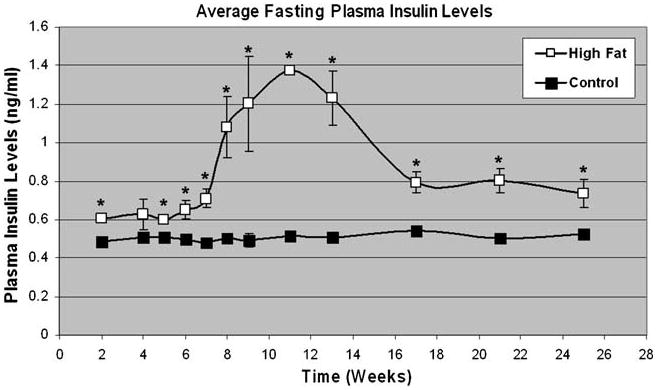
Effect of high-fat feeding on plasma insulin levels. Average plasma insulin concentrations of control (n=5) and high-fat fed (n=10) mice were plotted for the duration on the high-fat diet. Mice were fasted for 4 h and approximately 200 μL of tail blood was collected in heparinized capillary tubes and plasma was separated by centrifugation at 7,000×g for 10 min at 4°C and stored at −80°C. A part of the plasma samples was used to quantify insulin levels using an ultrasensitive rat/mouse insulin ELISA kit (ALPCO, Windham, NH, USA). Fasting plasma insulin levels were higher in high-fat fed mice except at 4-week time point and the highest level was observed between 8 and 13 weeks. Error bars represent the SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA. Single asterisk indicates p<0.05
