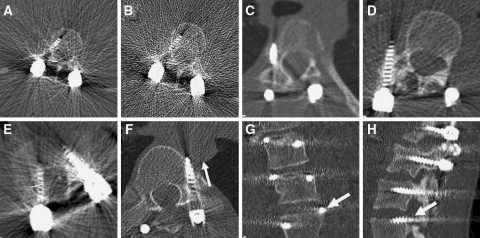
Fig. 2.
CT images showing some examples of screw placement and abnormal relationship of pedicle screws to the surrounding structures, which were encountered during the detailed analysis of the screw placement. a, b Axial images showing normally placed screw through the right pedicle of L1. Image a is reformatted with soft tissue algorithm, whereas image b is reformatted with skeletal algorithm, thus exhibiting increased noise. Image a with low signal-to-noise ratio was the image used during the evaluation of this study. c Axial image showing grade 2 LCP of a pedicle screw that passes totally lateral to the pedicle of T10 on the right side. d Axial image showing grade 2 LCP with paravertebral passage of pedicle screw which was supposed to pass through the right pedicle of L2. e Axial image showing the way of measurement of the degree of spinal canal encroachment of a medially placed pedicle screw. The encroachment is the distance between the medial pedicular cortex and the medial border of the medially placed screw, given in millimeter. f Axial image showing LCP and ACP of pedicle screw through T8 on the left side with screw tip touching the right and posterior margin of aorta (arrow). g Coronal image showing EPP through the upper endplate of L3 (arrow). h Sagittal image showing FP through the neural foramen above L3 on the left side (arrow)