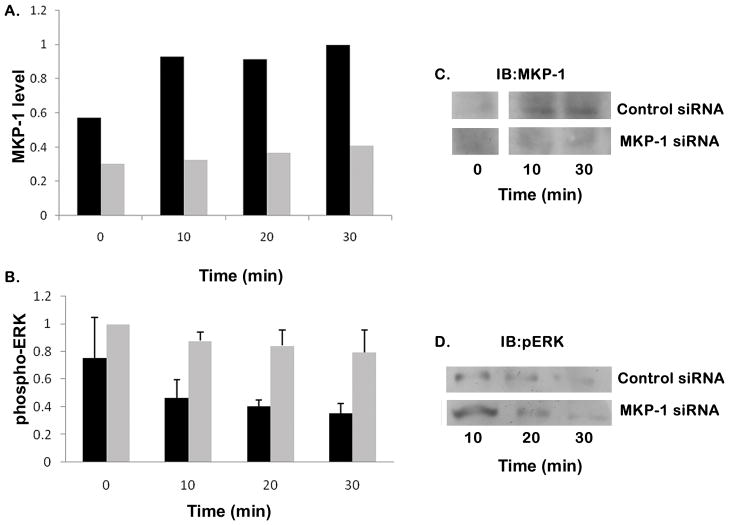
Figure 7. Inhibition of MKP-1 induction using siRNA protects ERK activity.
A7r5 cells were grown to 75% confluence and placed into transfection media for siRNA treatment as recommended. After transfection with either MKP-1 siRNA (light grey bars) or control siRNA (black bars), cells were placed back into regular growth media for recovery as recommended. After 24 hours recovery, cells were treated with 200 μg/ml heparin for varying times, harvested, and Western blots were developed for MKP-1 (panel A) and active ERK (panel B). Panel A represents a single experiment where the 30 min. MKP-1 level in cells with control siRNA was set as 1.0. The experiment in panel B was repeated four times and averages from these experiments are shown along with standard deviations. The active ERK levels in cells with MKP-1 siRNA were set at 1.0 for purposes of comparison and data analysis for the four experiments. The control siRNA samples contain significantly less active ERK than those samples treated with MKP-1 siRNA (p<0.05). Porcine VSMC treated with MKP-1 siRNA or control siRNA were treated with 200 μg/ml heparin for times noted and Western blots were developed with antibodies to MKP-1 (panel C). Panel D illustrates blotting for active ERK. Times shown represent time after heparin addition. To increase ERK activity, fresh serum was added (1% of total volume) 5 min after heparin. Antibodies against phospho-ERK were used for development.