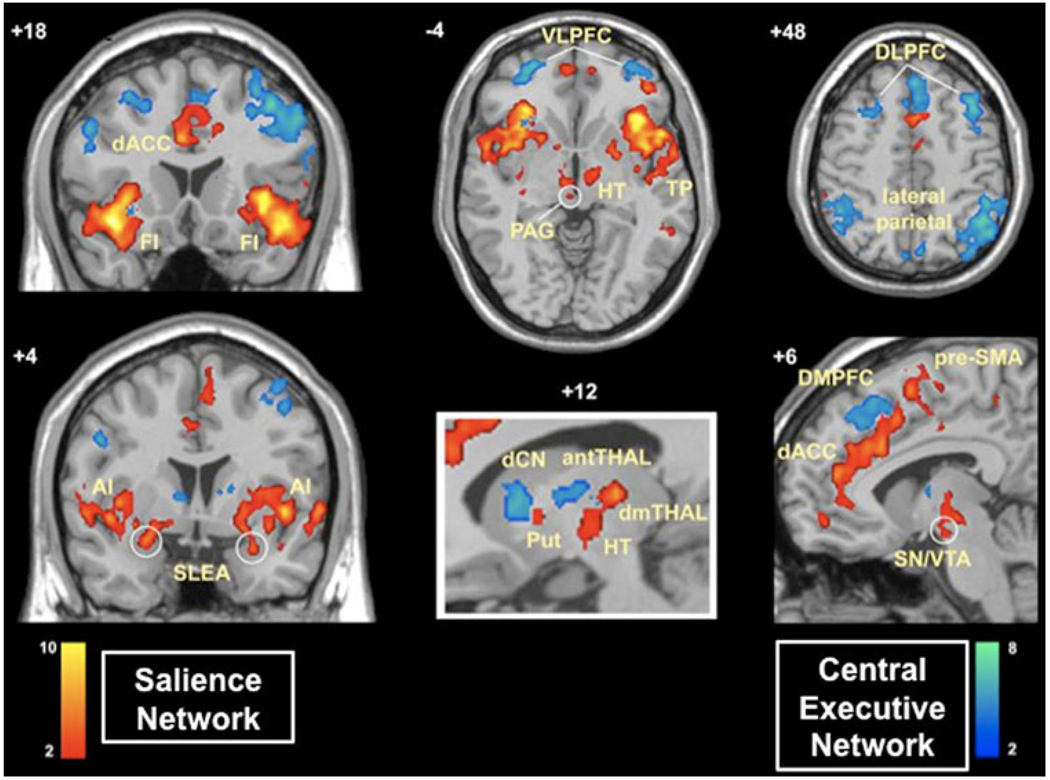
Fig. 2.
Two independent control networks identified using intrinsic physiological coupling in fMRI data. The salience network (shown in red) is important for monitoring the saliency of external inputs and internal brain events, and the central executive network (shown in blue) is engaged in higher-order cognitive and attentional control. The salience network is anchored in anterior insular and anterior cingulate cortices and features extensive connectivity with subcortical and limbic structures involved in reward and motivation. Central executive network links the dorsolateral frontal and parietal neocortices, with subcortical coupling that is distinct from that of the salience network (adapted from Seeley et al. 2007)