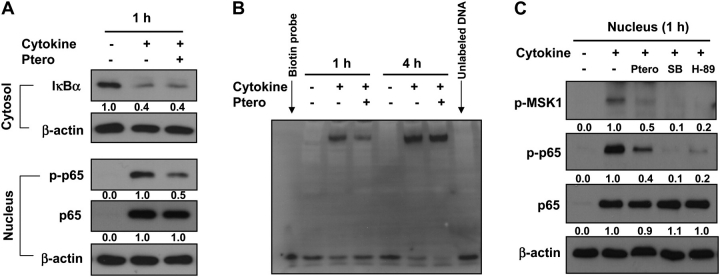
Fig. 5.
Effects of pterostilbene on the NF-κB pathway. (A) Pterostilbene lowers nuclear phospho-p65 levels in HT-29 cells. HT-29 cells (1.5 × 106 cells per 100 mm dish) were incubated with a mixture of TNF-α, interferon (IFN)-γ and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (each at 10 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of pterostilbene (30 μM) for 1 h, and cytosolic and nuclear protein fractions were collected and immunoblotted. (B) DNA binding of NF-κB is reduced by pterostilbene at 1 h. HT-29 cells were incubated with a mixture of TNF-α, IFN-γ and LPS together with pterostilbene (30 μM) for 1 or 4 h. NF-κB DNA-binding activity was determined by electrophoretic mobility shift assay. (C) Phosphorylation of p65 mediated through the p38/MSK-1 pathway is inhibited by pterostilbene in HT-29 cells. HT-29 cells were incubated with a mixture of TNF-α, IFN-γ and LPS in the presence or absence of pterostilbene (30 μM), MSK-1 inhibitor (H-89, 10 μM) or p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor (SB203580, 10 μM) for 1 h. The nuclear proteins were harvested and immunoblotted for phospho-MSK-1, phospho-p65 and p65. Quantification of western blots was done by ImagePro 6.2 program, and the numbers are given at the bottom of each western blot.