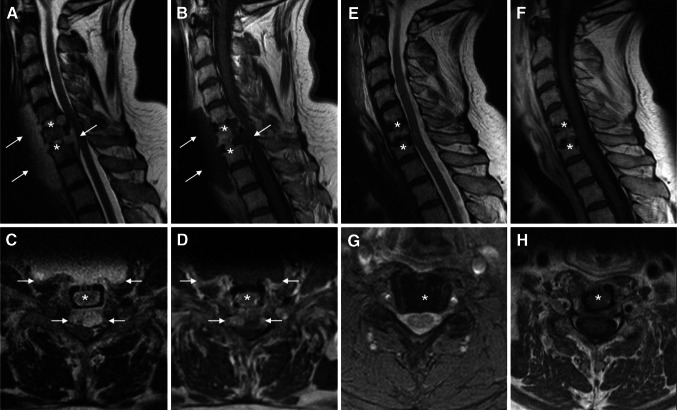
Fig. 1.
Time course of diagnostic imaging during cervical spondylodiscitis with an epidural component (a–d), after surgical decompression and ventral spondylodesis and subsequent targeted antibiotic therapy (e–h). a–d MRI in sagittal (a) and transversal (c) T2 sequence illustrates the mass effect of the acute spondylodiscitis with prevertebral and epidural abscess formation. Gadolinium enhanced T1 sequences in sagittal (b) and transversal (d) orientation demonstrate the contrasted rim and the hypointense, fluid center of the abscesses. The arrows label the margins of the prevertebral and epidural abscesses. The stars mark the former intervertebral disc spaces before cage interposition. e–h The postoperative MRI after 7 months clearly shows the totally decompressed spinal conditions. The sagittal (e) and transversal (g) T2 weighted images make the perimedullary rim of cerebrospinal fluid visible. The sagittal (f) and transversal (h) T1 weighted images after intravenous administration of gadolinium-DTPA illustrate the decreased inflammatory situation without any enhancement of gadolinium. The stars mark the levels of the intervertebral discs. The images belong to patient no. 4 from the Tables 1 and 2