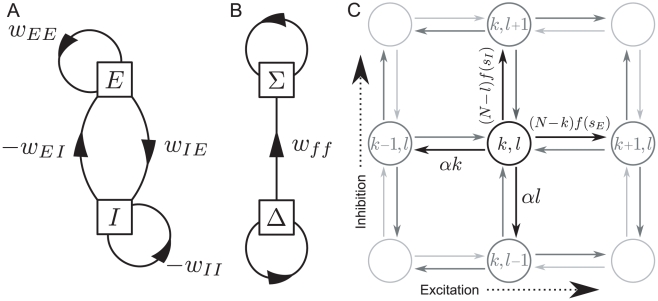
Figure 2. Network connectivity and dynamics.
A, schematic of connection strengths between excitatory, 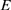 , and inhibitory,
, and inhibitory, 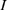 , populations, where an arrow indicates a synaptic input. B, schematic of functionally feedforward connectivity, where one mode of network excitation,
, populations, where an arrow indicates a synaptic input. B, schematic of functionally feedforward connectivity, where one mode of network excitation, 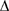 , excites another mode
, excites another mode  , but
, but  does not directly affect
does not directly affect 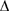 . C, network dynamics visualized. If there are
. C, network dynamics visualized. If there are 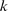 excitatory and
excitatory and  inhibitory neurons active, another excitatory neuron may become active, and network state moves rightwards one spot, at net rate
inhibitory neurons active, another excitatory neuron may become active, and network state moves rightwards one spot, at net rate 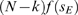 , where
, where 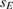 is the total synaptic input to an excitatory neuron. The rates for other transitions are shown with solid arrows and discussed in the population dynamics section of the results. Dashed arrows represent transitions into the state
is the total synaptic input to an excitatory neuron. The rates for other transitions are shown with solid arrows and discussed in the population dynamics section of the results. Dashed arrows represent transitions into the state 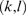 from adjacent states.
from adjacent states.