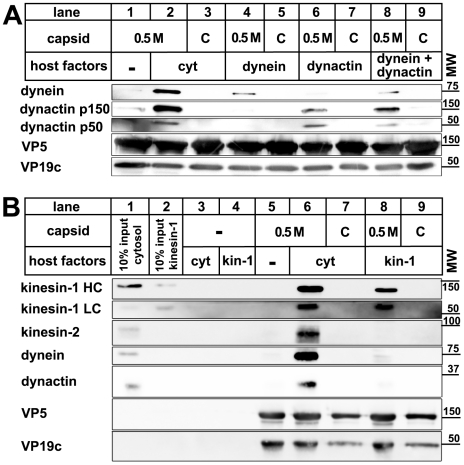
Figure 4. Dynein, dynactin, and kinesin-1 bind directly to tegumented HSV1 capsids.
HSV1 (F) capsids binding do dynein and or dynactin (A) or kinesin-1 (B) was analyzed as follows: HSV1(F) capsids generated by detergent lysis of extracellular virions in the presence of 0.5 M KCl, or nuclear C capsids were incubated with buffer (A: lane 1), 0.25 mg/ml pig brain cytosol (A: lanes 2 and 3), 15 µg/ml purified, native dynein (A: lanes 4 and 5), 15 µg/ml purified, native dynactin (A: lanes 6 and 7) or native dynein and dynactin (A: lanes 8 and 9) or with buffer (B: lane 5), 0.75 mg/ml pig brain cytosol (B: lanes 6 and 7) or 33 µg/ml purified, native kinesin-1 (B: lanes 8 and 9), and sedimented through a sucrose cushion. As controls, cytosol (B: lanes 1 and 3) or purified kinesin-1 (B: lanes 2 and 4) were also directly analyzed (B: lanes 1 and 2) or sedimented in the absence of capsids (B: lanes 3 and 4). Host proteins were detected by immunoblotting with antibodies against dynein (A & B: MAB1618 against intermediate chain), dynactin (A: mAb anti-p150, mAb anti-p50, B: anti-CapZβ mAb3F2.3), kinesin-1 (B: MAB1613 against heavy chain, MAB1616 against light chain), kinesin-2 (B: mAb against KAP3A). As loading controls, the samples were probed with antibodies against the capsid proteins VP5 (A and B: pAb NC-1) or VP19c (A and B: pAb NC-2). These blots show one of three independent experiments yielding similar results.