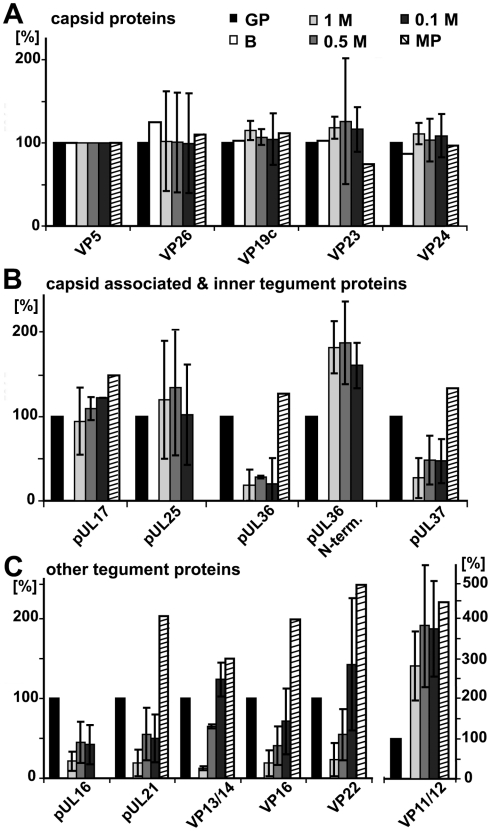
Figure 7. Mass spectrometric characterization of nuclear and viral HSV1 capsids.
The protein composition of HSV1 capsids (B: nuclear B capsids, viral capsids treated with 1.0, 0.5 or 0.1 M KCl), virions sedimented from cell culture supernatants (MP, medium pellet) and gradient purified virions (GP) were analyzed by quantitative mass spectrometry. A: the capsid proteins VP5, VP26, VP19c, VP23, VP24, B: the capsid-associated proteins pUL17 and pUL25 and the inner tegument proteins pUL36, an N-terminal fragment of pUL36, pUL37, pUL16, pUL21 and C: the other tegument proteins pUL16, pUL21, VP13/14, VP16, VP22 and VP11/12 were analyzed. The relative protein amount in a capsid or a virus preparation is given in comparison to the gradient purified virions set as 100%. Values lower than 100% indicate removal of a protein in the respective capsid or virus preparation, whereas values higher than 100% indicate a higher amount of this protein in capsid samples than in gradient purified virions. Values are normalized to the amount of the capsid protein VP5 to account for varying amounts of capsids in each sample. Mean values of three independent experiments are given for viral capsids treated with 1, 0.5 and 0.1 M KCl, and one experiment for medium pellet and nuclear B capsids. Error bars: SD. These data were after a further normalization also integrated into Fig. 3 (green columns).